Nextcloudは、無料の(オープンソース)Dropboxのようなソフトウェアであり、ownCloudプロジェクトのフォークです。 NextcloudはPHPとJavaScriptで記述されており、MySQL / MariaDB、PostgreSQL、Oracle Database、SQLiteなどの多くのデータベースシステムをサポートしています。
デスクトップと独自のサーバー間でファイルの同期を維持するために、Nextcloudは、Windows、Linux、およびMacデスクトップ用のアプリケーションと、AndroidおよびiOS用のモバイルアプリを提供します。 Nextcloudは単なるDropboxクローンではなく、カレンダー、連絡先、スケジュールタスク、Ampacheを使用したストリーミングメディアなどの追加機能を提供します。
このチュートリアルでは、Ubuntu 20.04サーバーに最新のNextcloudリリース(これを書いている時点では、最新のリリースは18です)をインストールして構成する方法を示します。 Nginx WebサーバーとPHP7.4-FPMを使用してNextcloudを実行し、データベースシステムとしてMariaDBサーバーを使用します。
- Ubuntu 20.04
- root権限
- NginxWebサーバーをインストールする
- PHP7.4-FPMのインストールと構成
- MySQLサーバーのインストールと構成
- SSLLetsencryptを生成する
- Nextcloud18をダウンロード
- Nextcloud用にNginx仮想ホストを構成する
- UFWファイアウォールの構成
- Nextcloudのインストール後
このnextcloudガイドで行う最初のステップは、NginxWebサーバーをインストールすることです。 ApacheWebサーバーの代わりにNginxWebサーバーを使用します。
サーバーにログインしてリポジトリを更新し、次に示すようにaptコマンドを使用してNginxWebサーバーをインストールします。
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx -y
インストールが完了したら、Nginxサービスを開始し、systemctlを使用してシステムの起動時に毎回サービスを起動できるようにします。
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx
Nginxサービスが稼働しています。次のコマンドを使用して、サービスを確認してください。
systemctl status nginx
そして、以下のような結果が得られます。
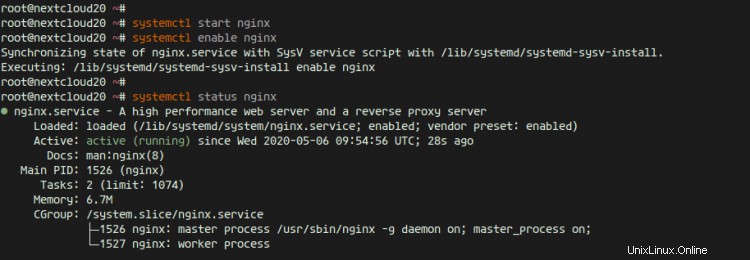
その結果、NginxWebサーバーがUbuntu20.04にインストールされました。
デフォルトでは、Ubuntu20.04にはデフォルトバージョンのPHP7.4が付属しています。
以下のaptコマンドを使用して、Nextcloudに必要なPHPおよびPHP-FPMパッケージをインストールします。
sudo apt install php-fpm php-curl php-cli php-mysql php-gd php-common php-xml php-json php-intl php-pear php-imagick php-dev php-common php-mbstring php-zip php-soap php-bz2 -y
インストールが完了したら、php-fpmとphp-cliのphp.iniファイルを構成します。
'/etc/php/7.4'ディレクトリに移動します。
cd /etc/php/7.4/
vimを使用してphp-fpmおよびphp-cliのphp.iniファイルを編集します。
vim fpm/php.ini
vim cli/php.ini
'date.timezone'行のコメントを解除し、独自のタイムゾーンで値を変更します。
date.timezone = Asia/Jakarta
'cgi.fix_pathinfo'行のコメントを解除し、値を'0'に変更します。
cgi.fix_pathinfo=0
保存して終了します。
次に、php-fpmプール構成「www.conf」を編集します。
vim fpm/pool.d/www.conf
以下の行のコメントを解除してください。
env[HOSTNAME] = $HOSTNAME env[PATH] = /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin env[TMP] = /tmp env[TMPDIR] = /tmp env[TEMP] = /tmp
保存して終了します。
PHP7.4-FPMサービスを再起動し、システムの起動時に毎回起動できるようにします。
systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
systemctl enable php7.4-fpm
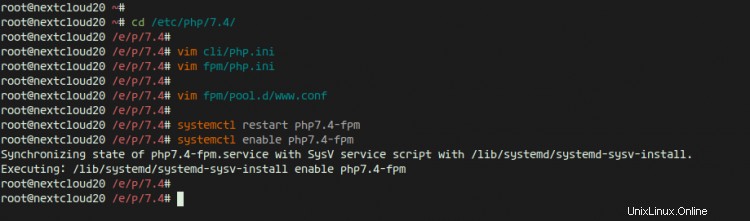
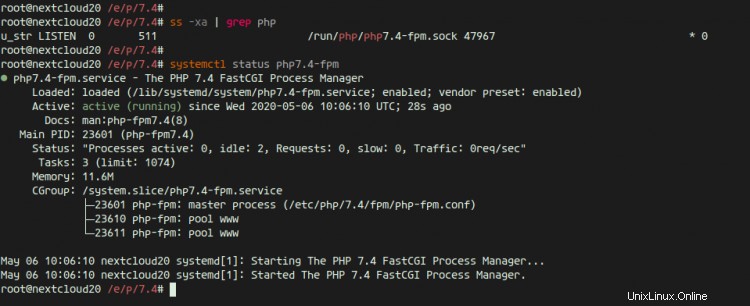
次に、次のコマンドを使用してPHP-FPMサービスを確認します。
ss -xa | grep php
systemctl status php7.4-fpm
そして、php-fpmがsockファイル'/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock'の下で稼働していることがわかります。
このステップでは、最新のMariaDBバージョンをインストールし、nextcloudインストール用の新しいデータベースを作成します。最新バージョンのMariaDBパッケージは、デフォルトでリポジトリで利用できます。
以下のaptコマンドを使用してMariaDBサーバーの最新バージョンをインストールします。
sudo apt install mariadb-server -y
インストールが完了したら、MariaDBサービスを開始し、システムの起動時に毎回起動できるようにします。
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb
次に、次のコマンドを使用してMySQLサービスを確認します。
systemctl status mariadb
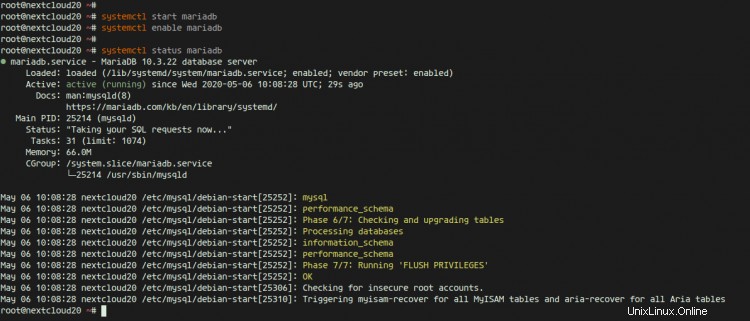
MariaDBサーバーはUbuntu20.04で稼働しています。
次に、「mysql_secure_installation」コマンドを使用してMariaDBルートパスワードを構成します。
次のコマンドを実行します。
mysql_secure_installation
そして、MariaDBサーバーの構成を求められます。また、MariaDBサーバーの新しいルートパスワードを入力します。
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Press Enter
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
そして、MariaDBルートパスワードが設定されました。
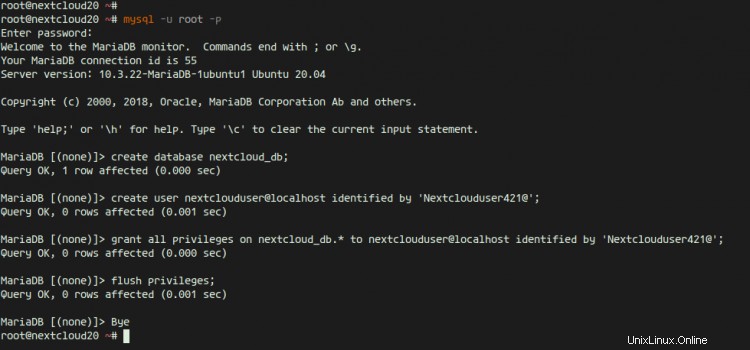
次に、nextcloudインストール用の新しいデータベースを作成します。ユーザー「nextclouduser」とパスワード「[emailprotected]」を使用して「nextcloud_db」という名前の新しいデータベースを作成します。
mysqlコマンドを使用してrootユーザーとしてMySQLシェルにログインします。
mysql -u root -p
TYPE THE MYSQL ROOT PASSWORD
次に、次のMySQLクエリを実行して、パスワードを使用してデータベースとユーザーを作成します。
create database nextcloud_db;
create user [email protected] identified by '[email protected]';
grant all privileges on nextcloud_db.* to [email protected] identified by '[email protected]';
flush privileges;
そして、nextcloudインストール用の新しいデータベースとユーザーが作成されました。
nextcloudのMariaDBのインストールと構成が完了しました。
このチュートリアルでは、Letsencryptの無料SSLを使用してnextcloudを保護し、letsencryptツールを使用して証明書ファイルを生成します。
ドメイン名がない場合、またはローカルコンピューターにnextcloudをインストールしていない場合は、OpenSSLを使用して自己署名証明書を生成できます。
以下のaptコマンドを使用して「letsencrypt」ツールをインストールします。
sudo apt install certbot -y
インストールが完了したら、nginxサービスを停止します。
systemctl stop nginx
次に、cerbotコマンドラインを使用して、ドメイン名「nextcloud.hakase-labs.io」のSSL証明書を生成します。以下のコマンドを実行します。
certbot certonly --standalone -d cloud.hakase-labs.io
メールアドレスの入力を求められ、更新通知に使用されます。 Letsencrypt TOS契約の場合は「A」と入力して同意し、共有メールアドレスの場合は「N」と入力して「いいえ」と入力します。
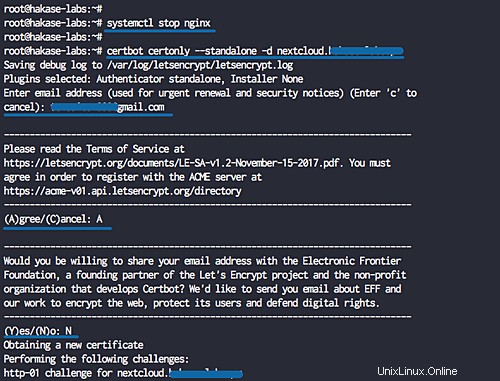
完了すると、次のような結果が得られます。
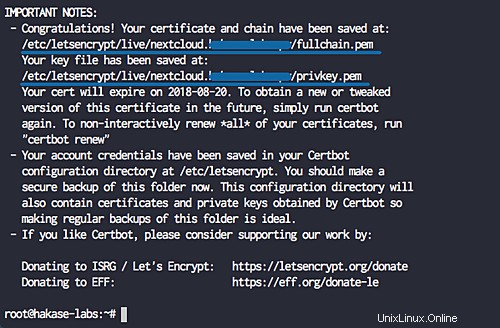
netxcloudドメイン名のSSL証明書Letsencryptが生成されました。これらはすべて、「/ etc /letsencrypt / live/your-domain」ディレクトリにあります。
nextcloudソースコードをダウンロードする前に、unzipパッケージがシステムにインストールされていることを確認してください。パッケージがない場合は、以下のaptコマンドを使用してインストールしてください。
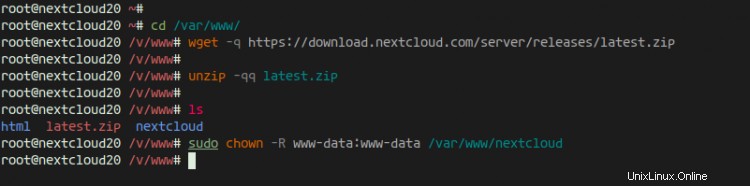
sudo apt install wget unzip zip -y
次に、「/ var / www」ディレクトリに移動し、次のコマンドを使用してNextcloudの最新バージョンをダウンロードします。
cd /var/www/
wget -q https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/latest.zip
Nextcloudソースコードを抽出すると、新しいディレクトリ「netxcloud」が取得され、nextcloudディレクトリの所有権がユーザー「www-data」に変更されます。
unzip -qq latest.zip
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/nextcloud
その結果、Nextcloudは「/ var / www / nextcloud」ディレクトリの下にダウンロードされ、Webルートディレクトリになります。
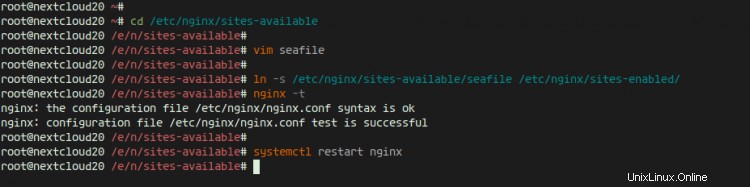
このステップでは、nextcloud用にnginx仮想ホストを構成します。 HTTPS接続で実行するようにnextcloudを構成し、HTTP接続を安全なHTTPS接続に自動的に強制します。
次に、「/ etc / nginx / sites-available」ディレクトリに移動し、新しい仮想ホストファイル「nextcloud」を作成します。
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
vim nextcloud
そこに、次のnextcloud仮想ホスト構成を貼り付けます。
upstream php-handler {
#server 127.0.0.1:9000;
server unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name cloud.hakase-labs.io;
# enforce https
return 301 https://$server_name:443$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name cloud.hakase-labs.io;
# Use Mozilla's guidelines for SSL/TLS settings
# https://mozilla.github.io/server-side-tls/ssl-config-generator/
# NOTE: some settings below might be redundant
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/cloud.hakase-labs.io/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/cloud.hakase-labs.io/privkey.pem;
# Add headers to serve security related headers
# Before enabling Strict-Transport-Security headers please read into this
# topic first.
#add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000; includeSubDomains; preload;" always;
#
# WARNING: Only add the preload option once you read about
# the consequences in https://hstspreload.org/. This option
# will add the domain to a hardcoded list that is shipped
# in all major browsers and getting removed from this list
# could take several months.
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-Download-Options "noopen" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies "none" always;
add_header X-Robots-Tag "none" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
# Remove X-Powered-By, which is an information leak
fastcgi_hide_header X-Powered-By;
# Path to the root of your installation
root /var/www/nextcloud;
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# The following 2 rules are only needed for the user_webfinger app.
# Uncomment it if you're planning to use this app.
#rewrite ^/.well-known/host-meta /public.php?service=host-meta last;
#rewrite ^/.well-known/host-meta.json /public.php?service=host-meta-json last;
# The following rule is only needed for the Social app.
# Uncomment it if you're planning to use this app.
#rewrite ^/.well-known/webfinger /public.php?service=webfinger last;
location = /.well-known/carddav {
return 301 $scheme://$host:$server_port/remote.php/dav;
}
location = /.well-known/caldav {
return 301 $scheme://$host:$server_port/remote.php/dav;
}
# set max upload size
client_max_body_size 512M;
fastcgi_buffers 64 4K;
# Enable gzip but do not remove ETag headers
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private no_last_modified no_etag auth;
gzip_types application/atom+xml application/javascript application/json application/ld+json application/manifest+json application/rss+xml application/vnd.geo+json application/vnd.ms-fontobject application/x-font-ttf application/x-web-app-manifest+json application/xhtml+xml application/xml font/opentype image/bmp image/svg+xml image/x-icon text/cache-manifest text/css text/plain text/vcard text/vnd.rim.location.xloc text/vtt text/x-component text/x-cross-domain-policy;
# Uncomment if your server is build with the ngx_pagespeed module
# This module is currently not supported.
#pagespeed off;
location / {
rewrite ^ /index.php;
}
location ~ ^\/(?:build|tests|config|lib|3rdparty|templates|data)\/ {
deny all;
}
location ~ ^\/(?:\.|autotest|occ|issue|indie|db_|console) {
deny all;
}
location ~ ^\/(?:index|remote|public|cron|core\/ajax\/update|status|ocs\/v[12]|updater\/.+|oc[ms]-provider\/.+)\.php(?:$|\/) {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\.php)(\/.*|)$;
set $path_info $fastcgi_path_info;
try_files $fastcgi_script_name =404;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $path_info;
fastcgi_param HTTPS on;
# Avoid sending the security headers twice
fastcgi_param modHeadersAvailable true;
# Enable pretty urls
fastcgi_param front_controller_active true;
fastcgi_pass php-handler;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_request_buffering off;
}
location ~ ^\/(?:updater|oc[ms]-provider)(?:$|\/) {
try_files $uri/ =404;
index index.php;
}
# Adding the cache control header for js, css and map files
# Make sure it is BELOW the PHP block
location ~ \.(?:css|js|woff2?|svg|gif|map)$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=15778463";
# Add headers to serve security related headers (It is intended to
# have those duplicated to the ones above)
# Before enabling Strict-Transport-Security headers please read into
# this topic first.
#add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000; includeSubDomains; preload;" always;
#
# WARNING: Only add the preload option once you read about
# the consequences in https://hstspreload.org/. This option
# will add the domain to a hardcoded list that is shipped
# in all major browsers and getting removed from this list
# could take several months.
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-Download-Options "noopen" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies "none" always;
add_header X-Robots-Tag "none" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
# Optional: Don't log access to assets
access_log off;
}
location ~ \.(?:png|html|ttf|ico|jpg|jpeg|bcmap)$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
# Optional: Don't log access to other assets
access_log off;
}
} 保存して終了します。
仮想ホストを有効にして構成をテストし、エラーがないことを確認します。
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/nextcloud /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
nginx -t
次に、以下のsystemctlコマンドを使用してPHP7.4-FPMサービスとnginxサービスを再起動します。
systemctl restart nginx
systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
nextcloudのNginx仮想ホスト構成が作成されました。
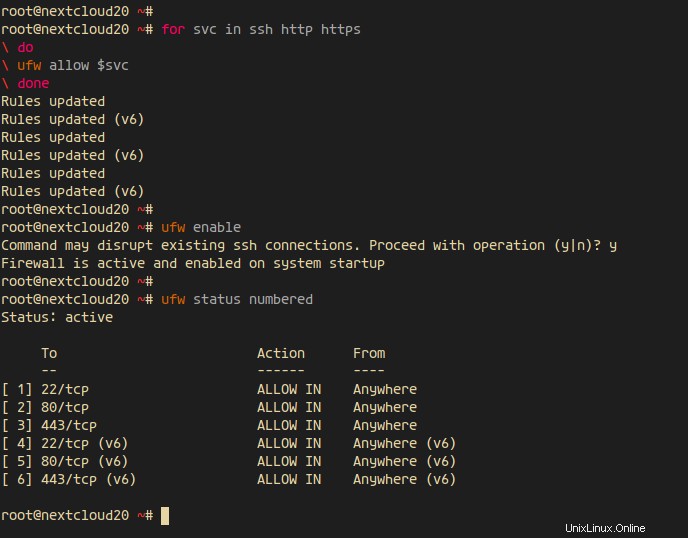
このチュートリアルでは、ファイアウォールをオンにし、UbuntuにUFWファイアウォールを使用します。
以下のコマンドを使用して、SSH、HTTP、HTTPSをUFWファイアウォールリストに追加します。
for svc in ssh http https
do
ufw allow $svc
done
その後、UFWファイアウォールを有効にして、許可されているサービスとポートを確認します。
ufw enable
ufw status numbered
そして、HTTPポート80を取得し、HTTPSポート443がリストに含まれます。
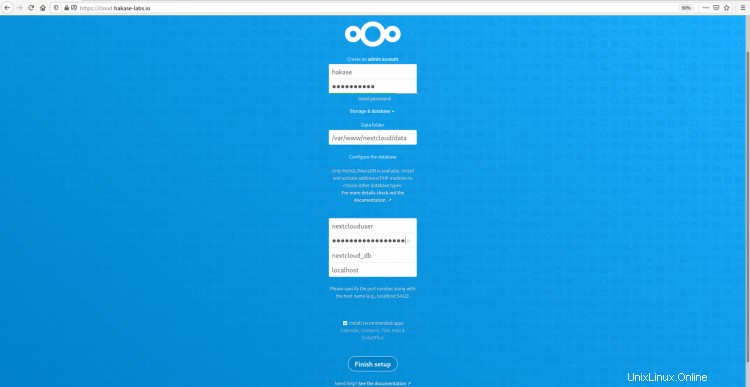
ウェブブラウザを開き、nextcloudのURLアドレスを入力します。
http://cloud.hakase-labs.io/
そして、安全なHTTPS接続にリダイレクトされます。
トップページで、nextcloudの管理者ユーザーを作成し、管理者ユーザーのパスワードを入力する必要があります。 「データフォルダ」設定で、「データ」ディレクトリのフルパス「/ var / www / nextcloud/data」を入力します。
ページを一番下までスクロールすると、データベース構成が表示されます。手順3で作成したデータベース情報を入力し、[セットアップの完了]ボタンをクリックします。
[おすすめのアプリをインストールする]オプションをオンにすると、次のページが表示されます。
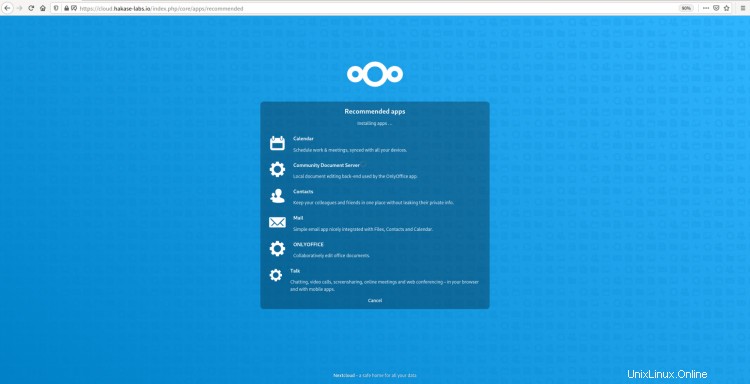
Nextcloudはあなたに追加の推奨アプリケーションをインストールしています。
インストールが完了すると、次のようなNextcloudダッシュボードが表示されます。
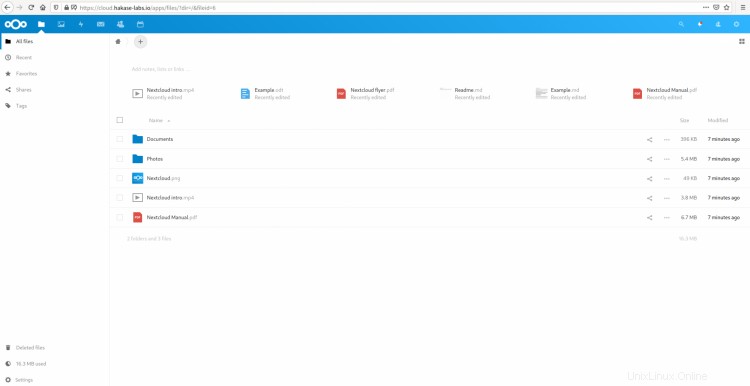
Ubuntu20.04でのNginxWebサーバーとMySQLデータベースを使用したNextcloud18のインストールが正常に完了しました。