パーフェクトサーバー-Ubuntu12.04LTS(Apache2、BIND、Dovecot、ISPConfig 3)
このチュートリアルでは、ISPConfig3をインストールするためにUbuntu12.04 LTS(Precise Pangolin)サーバー(Apache2、BIND、Dovecotを使用)を準備する方法と、ISPConfig3をインストールする方法を示します。 Webブラウザを介した次のサービス:Apacheまたはnginx Webサーバー、Postfixメールサーバー、CourierまたはDovecot IMAP / POP3サーバー、MySQL、BINDまたはMyDNSネームサーバー、PureFTPd、SpamAssassin、ClamAVなど。このセットアップは、Apache(nginxの代わりに)、BIND(MyDNSの代わりに)、およびDovecot(Courierの代わりに)を対象としています。
この設定はISPConfig2では機能しないことに注意してください ! ISPConfig 3でのみ有効です!
これがあなたのために働くという保証はありません!
ISPConfig3マニュアル
ISPConfig 3の使用方法を学ぶために、ISPConfig3マニュアルをダウンロードすることを強くお勧めします。
300ページ以上で、ISPConfig(管理者、再販業者、クライアント)の背後にある概念をカバーし、ISPConfig 3をインストールおよび更新する方法を説明し、有効な入力の例とともにISPConfigのすべてのフォームとフォームフィールドのリファレンスを含み、チュートリアルを提供しますISPConfig 3の最も一般的なタスクについても説明します。また、サーバーをより安全にする方法を示し、最後にトラブルシューティングのセクションがあります。
Android用ISPConfigモニターアプリ
ISPConfig Monitor Appを使用すると、サーバーのステータスを確認し、すべてのサービスが期待どおりに実行されているかどうかを確認できます。 TCPおよびUDPポートを確認し、サーバーにpingを実行できます。さらに、このアプリを使用して、ISPConfigがインストールされているサーバーに詳細を要求できます(ISPConfigモニターアプリをサポートするインストール済みのISPConfig3の最小バージョンは3.0.3.3です! );これらの詳細には、ISPConfigコントロールパネルのモニターモジュールから知っているすべてのもの(サービス、メールとシステムのログ、メールキュー、CPUとメモリの情報、ディスク使用量、クォータ、OSの詳細、RKHunterログなど)が含まれます。 、ISPConfigはマルチサーバー対応であるため、ISPConfigマスターサーバーから制御されているすべてのサーバーを確認できます。
ダウンロードと使用方法については、http://www.ispconfig.org/ispconfig-3/ispconfig-monitor-app-for-android/にアクセスしてください。
1要件
このようなシステムをインストールするには、次のものが必要です。
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTSサーバーCD、ここで入手可能:http://releases.ubuntu.com/releases/12.04/ubuntu-12.04-server-i386.iso(i386)またはhttp://releases.ubuntu.com/リリース/12.04/ubuntu-12.04-server-amd64.iso(x86_64)
- 高速インターネット接続。
2予備メモ
このチュートリアルでは、ホスト名server1.example.comとIPアドレス192.168.0.100およびゲートウェイ192.168.0.1を使用します。これらの設定はユーザーによって異なる場合があるため、必要に応じて置き換える必要があります。
3ベースシステム
UbuntuインストールCDをシステムに挿入し、そこから起動します。言語を選択してください:
次に、[Ubuntuサーバーのインストール]を選択します:
言語をもう一度選択してください(?):
次に、場所を選択します:

言語と場所の珍しい組み合わせ(私の場合のように、言語として英語、場所としてドイツなど)を選択した場合、インストーラーは、この組み合わせにロケールが定義されていないことを通知する場合があります。この場合、ロケールを手動で選択する必要があります。ここでen_US.UTF-8を選択します:
キーボードレイアウトを選択します(いくつかのキーを押すように求められ、インストーラーは押したキーに基づいてキーボードレイアウトを検出しようとします):
インストーラーはインストールCDとハードウェアをチェックし、ネットワークにDHCPサーバーがある場合はDHCPを使用してネットワークを構成します。
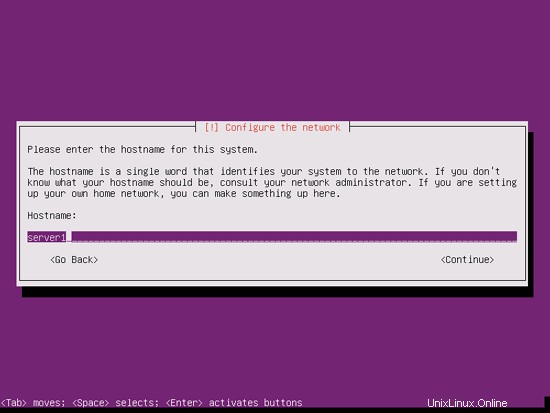
ホスト名を入力します。この例では、私のシステムの名前は server1.example.comです。 、だから私は server1と入力します :
ユーザーを作成します。たとえば、ユーザー名administratorを使用してユーザーAdministratorを作成します(Ubuntu 12.04では予約名であるため、ユーザー名adminは使用しないでください):
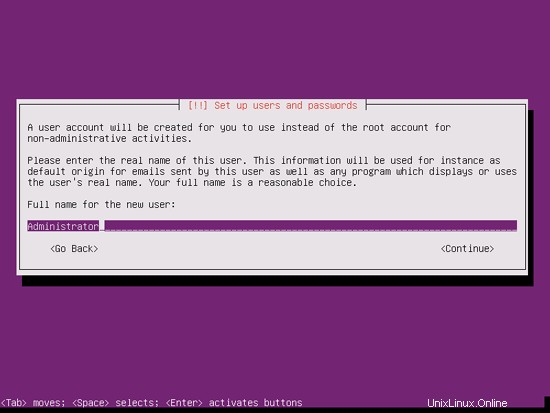
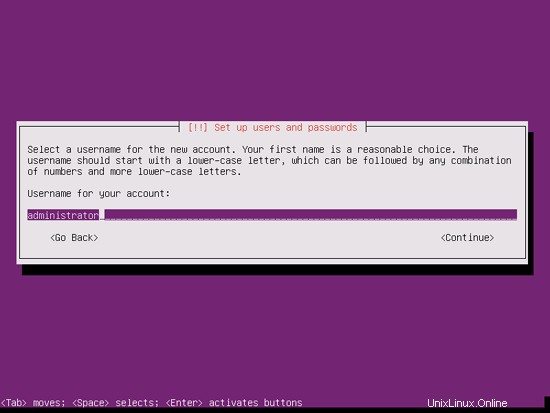
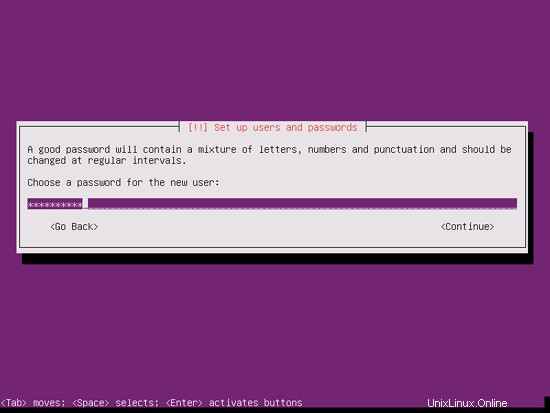
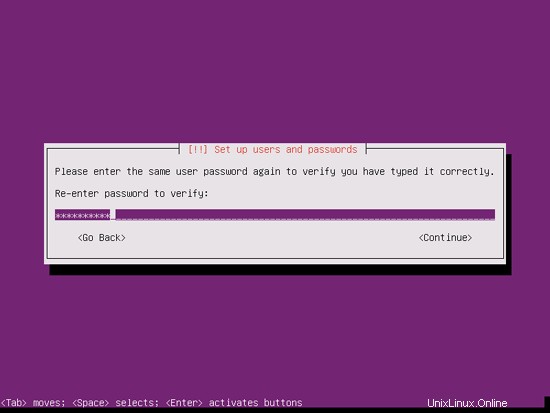
完璧なサーバー-Ubuntu12.04LTS(Apache2、BIND、Dovecot、ISPConfig 3)-ページ2
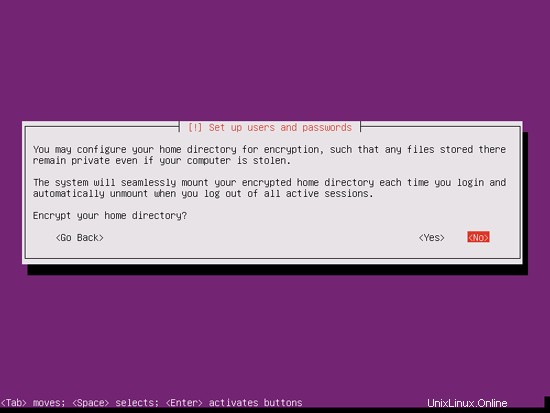
暗号化されたプライベートディレクトリは必要ないので、ここでは[いいえ]を選択します:
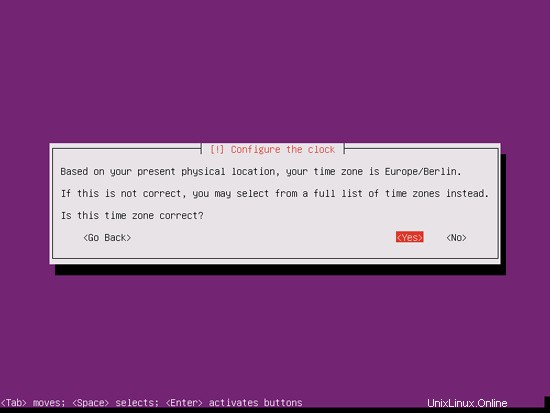
インストーラーがタイムゾーンを正しく検出したかどうかを確認してください。その場合は[はい]を選択し、そうでない場合は[いいえ]を選択します:
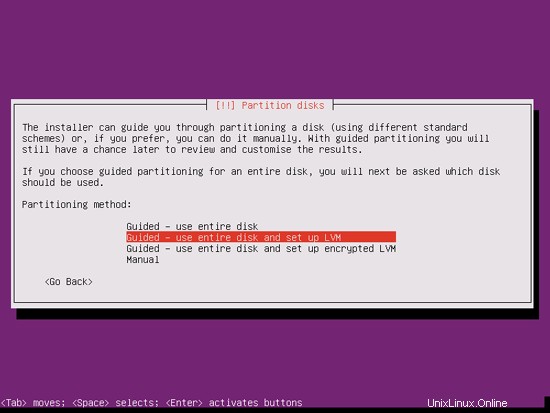
次に、ハードディスクをパーティション分割する必要があります。簡単にするために、ガイド付きを選択します-ディスク全体を使用してLVMをセットアップします-これにより、2つの論理ボリュームを持つ1つのボリュームグループが作成されます.1つは/ファイルシステム用、もう1つはスワップ用です(もちろん、パーティショニングは完全にあなた次第です-もし何をしているのかがわかっているので、パーティションを手動で設定することもできます。
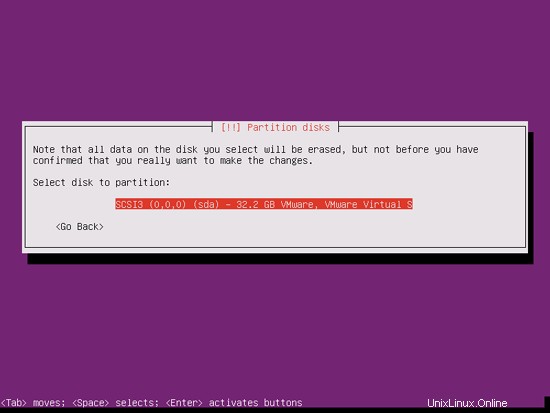
パーティションを作成するディスクを選択します:
「ディスクに変更を書き込んでLVMを構成しますか?」というメッセージが表示されたら、「はい」を選択します:
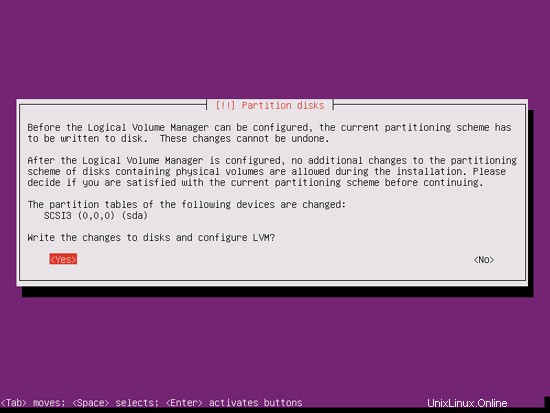
[ガイド付き]を選択した場合-ディスク全体を使用してLVMをセットアップすると、パーティショナーはすべてのディスクスペースを使用する1つの大きなボリュームグループを作成します。これで、/およびスワップの論理ボリュームがそのディスクスペースのどれだけを使用するかを指定できます。後で既存の論理ボリュームを拡張したり、新しい論理ボリュームを作成したりできるように、スペースを未使用のままにしておくことは理にかなっています。これにより、柔軟性が向上します。
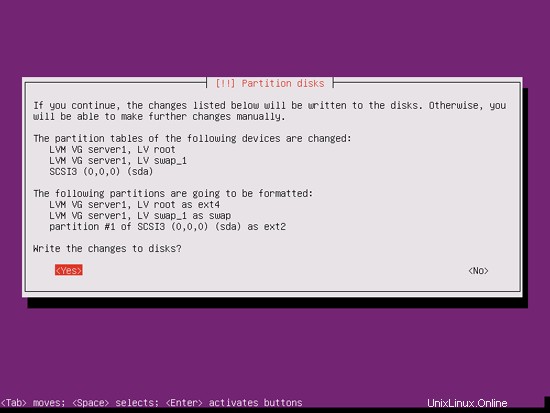
終了したら、[ディスクに変更を書き込みますか?:
]というメッセージが表示されたら、[はい]をクリックします。

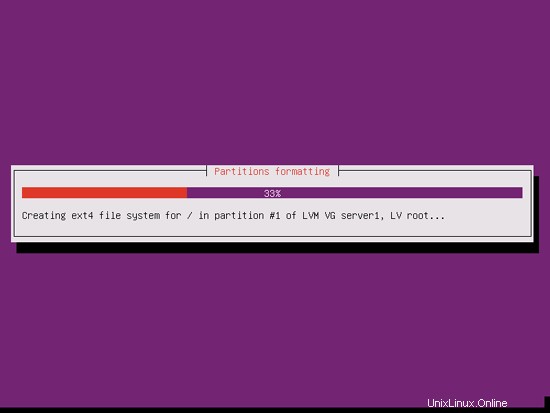
その後、新しいパーティションが作成され、フォーマットされます:
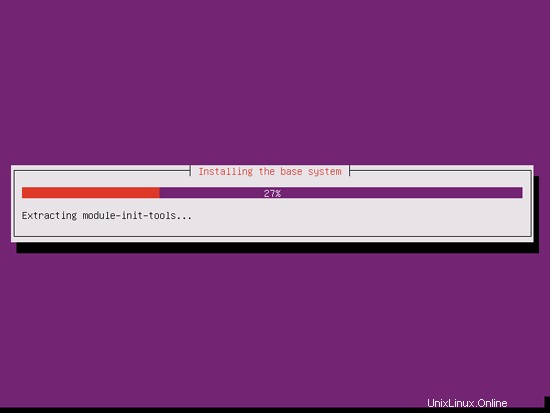
これでベースシステムがインストールされました:
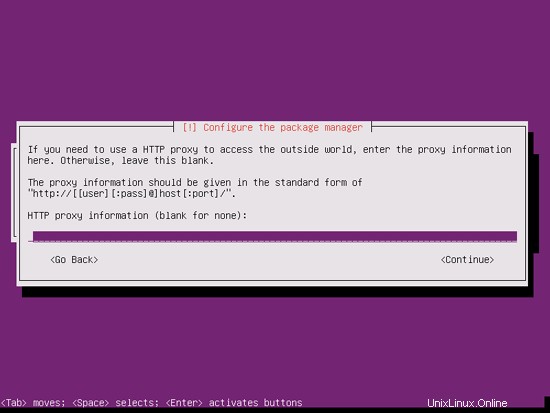
次に、パッケージマネージャーaptが構成されます。プロキシサーバーを使用してインターネットに接続している場合を除き、HTTPプロキシ行は空のままにします。
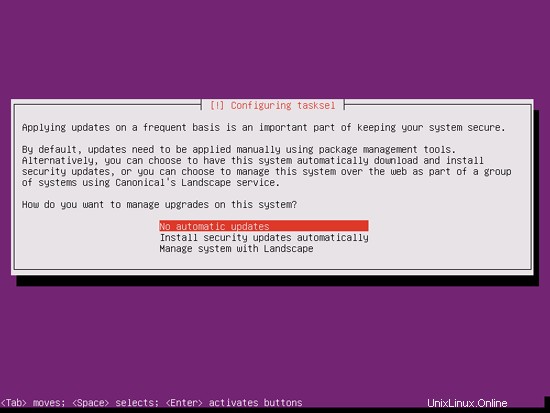
私は少し古風で、サーバーを手動で更新してより詳細に制御するのが好きなので、[自動更新なし]を選択します。もちろん、ここで何を選択するかはあなた次第です:
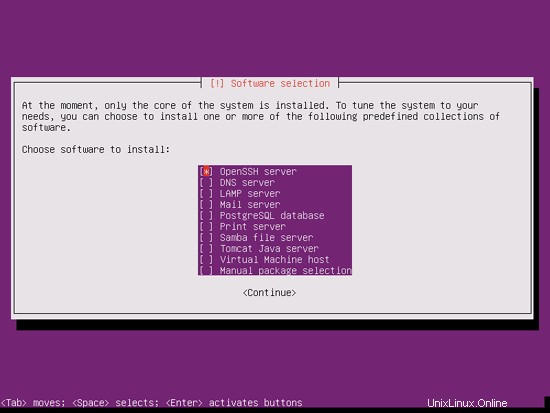
DNS、メール、LAMPサーバーが必要ですが、システムにインストールするものを完全に制御したいので、今はそれらを選択しません。必要なパッケージは後で手動でインストールします。ここで選択するのはOpenSSHサーバーだけなので、インストールが完了したらすぐにPuTTYなどのSSHクライアントを使用してシステムに接続できます。
インストールは続行されます:
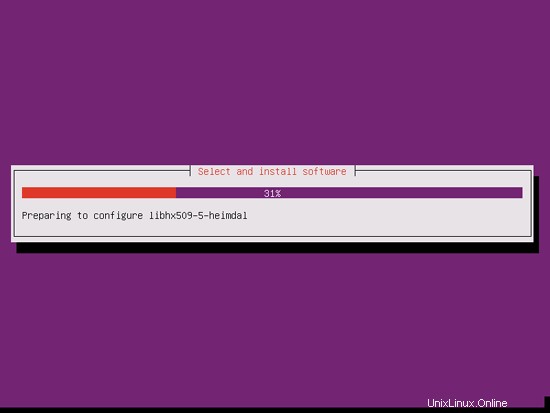
GRUBブートローダーがインストールされます:
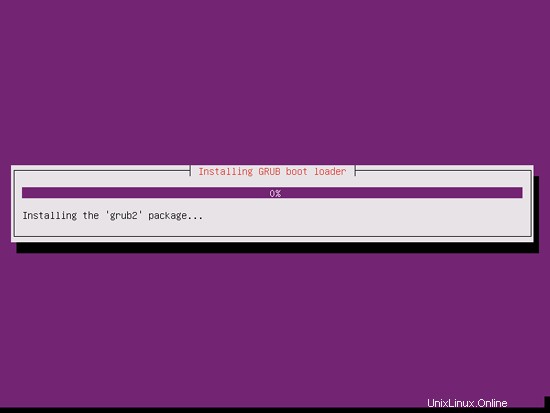
GRUBブートローダーをマスターブートレコードにインストールしますか?:
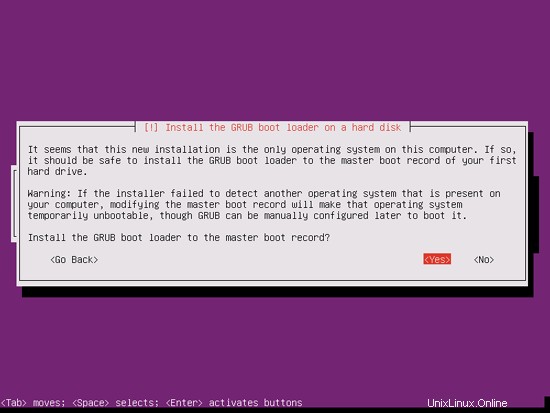
これで基本システムのインストールは完了です。インストールCDをCDドライブから取り出し、[続行]をクリックしてシステムを再起動します。
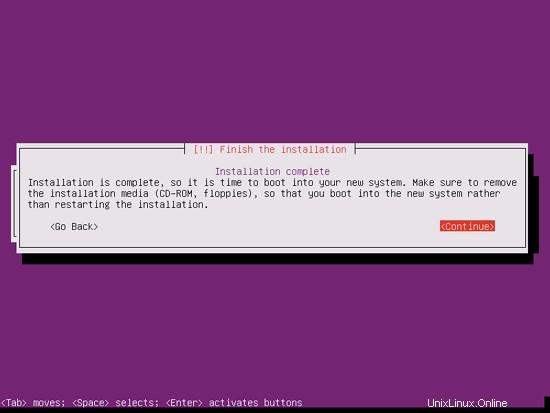
次のステップに進みます...
完璧なサーバー-Ubuntu12.04LTS(Apache2、BIND、Dovecot、ISPConfig 3)-ページ3
4ルート権限を取得する
再起動後、以前に作成したユーザー名(管理者など)でログインできます。このチュートリアルのすべてのステップをroot権限で実行する必要があるため、このチュートリアルのすべてのコマンドの前に文字列sudoを付けるか、「
」と入力して今すぐrootになります。sudo su
(実行してルートログインを有効にすることもできます
sudo passwd root
ルートにパスワードを与えます。その後、rootとして直接ログインできますが、これはさまざまな理由でUbuntu開発者やコミュニティに嫌われています。 http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=765414を参照してください。)
5 SSHサーバーのインストール(オプション)
システムのインストール中にOpenSSHサーバーをインストールしなかった場合は、今すぐインストールできます。
apt-get install ssh openssh-server
今後は、PuTTYなどのSSHクライアントを使用して、ワークステーションからUbuntu 12.04サーバーに接続し、このチュートリアルの残りの手順に従うことができます。
6 vim-noxをインストールします(オプション)
このチュートリアルでは、テキストエディタとしてviを使用します。デフォルトのviプログラムは、UbuntuとDebianで奇妙な動作をします。これを修正するには、vim-noxをインストールします:
apt-get install vim-nox
(joeやnanoなどの別のテキストエディタを使用する場合は、これを行う必要はありません。)
7ネットワークの構成
UbuntuインストーラーはDHCP経由でネットワーク設定を取得するようにシステムを構成しているため、サーバーには静的IPアドレスが必要であるため、ここで変更する必要があります。 / etc / network / interfacesを編集します 必要に応じて調整します(このセットアップ例では、IPアドレス 192.168.0.100を使用します また、DNSサーバー8.8.8.8および8.8.4.4-Ubuntu 12.04以降、/ etc / resolv.confを直接編集することはできなくなりましたが、ネットワーク構成でネームサーバーを指定する必要があります-
を参照してください。man resolvconf
詳細については):
vi / etc / network / interfaces
#このファイルには、システムで使用可能なネットワークインターフェイス#とそれらをアクティブ化する方法が記載されています。詳細については、interfaces(5)を参照してください。#ループバックネットワークinterfaceauto loiface lo inet loopback#プライマリネットワークinterfaceauto eth0ifaceeth0inet静的アドレス192.168.0.100ネットマスク255.255.255.0ネットワーク192.168.0.0ブロードキャスト192.168.0.255ゲートウェイ192.168.0.1dns-ネームサーバー8.8.8.88.8.4.4 |
次に、ネットワークを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/networking restart
次に、/ etc/hostsを編集します。次のようにします:
vi / etc / hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost192.168.0.100 server1.example.com server1#IPv6対応ホストには次の行が望ましいです。:1ip6 -localhost ip6-loopbackfe00 ::0 ip6-localnetff00 ::0 ip6-mcastprefixff02 ::1 ip6-allnodesff02 ::2 ip6-allrouters |
今すぐ実行
echo server1.example.com> / etc / hostname
/etc/init.d/hostname restart
その後、実行します
hostname
hostname -f
両方ともserver1.example.comが表示されるはずです。
8/etc/apt/sources.listを編集してLinuxインストールを更新する
/etc/apt/sources.listを編集します。コメントアウトするか、ファイルからインストールCDを削除し、ユニバースおよびマルチバースリポジトリが有効になっていることを確認します。次のようになります:
vi /etc/apt/sources.list
## deb cdrom:[Ubuntu-Server 12.04 LTS _Precise Pangolin_-リリースamd64(20120424.1)] / dists / Precision / main / binary-i386 / #deb cdrom:[Ubuntu-Server 12.04 LTS _Precise Pangolin_-Release amd64(20120424.1)] / dists / Precision / restarted / binary-i386 /#deb cdrom:[Ubuntu-Server 12.04 LTS _Precise Pangolin_-Release amd64(20120424.1)] /正確なメインrestricted#deb cdrom:[Ubuntu-Server 12.04 LTS _Precise Pangolin_-リリースamd64(20120424.1)] / dists / Precision / main / binary-i386 /#deb cdrom:[Ubuntu-Server 12.04 LTS _Precise Pangolin_-リリースamd64(20120424.1) )] / dists / Precision / Restricted / binary-i386 /#deb cdrom:[Ubuntu-Server 12.04 LTS _Precise Pangolin_-Release amd64(20120424.1)] / Accurate Main Restricted#http://help.ubuntu.com/community/を参照ディストリビューションの#新しいバージョンにアップグレードする方法に関するアップグレードノートhttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/正確なメインrestricteddeb-srchttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/正確なメイン制限##主要なバグ修正upd ## distribution.deb http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/precision-updates mainstricteddeb-srchttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/precision-の最終リリース後に生成されたateメイン制限付きアップデート##N.B.このリポジトリのソフトウェアは、Ubuntu##チームによって完全にサポートされていません。また、ユニバースのソフトウェアは、Ubuntuセキュリティチームから##レビューやアップデートを受け取らないことに注意してください。debhttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/正確なuniversedeb-src http://de.archive。 ubuntu.com/ubuntu/正確なuniversedebhttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/precision-updatesuniversedeb-src http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/precision-updates universe ## N.B.このリポジトリのソフトウェアは、Ubuntu ##チームによって完全にサポートされておらず、無料のライセンスが適用されていない可能性があります。 ##ソフトウェアを使用する権利についてご満足ください。また、## multiverseのソフトウェアは、Ubuntu##セキュリティチームからレビューやアップデートを受け取らないことに注意してください。debhttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/正確なmultiversedeb-src http://de。 archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/正確なmultiversedebhttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/precision-updatesmultiversedeb-src http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/precision-updates multiverse ## N.B.このリポジトリのソフトウェアは、メインリリースに含まれているものほど広範囲にテストされていない可能性がありますが、##便利な機能を提供する可能性のある一部のアプリケーションの新しいバージョンが含まれています。##また、バックポートのソフトウェアは受信しないことに注意してくださいレビュー##またはUbuntuセキュリティチームからのアップデート.debhttp://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/exact-backportsメイン制限付きユニバースmultiversedeb-src http://de.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/正確なバックポートメイン制限付きユニバースmultiversedebhttp://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu正確なセキュリティメインrestricteddeb-srchttp://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu正確なセキュリティメインrestricteddebhttp://security.ubuntu.com / ubuntuprecision-security universedeb-src http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntuprecision-security universedeb http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntuprecision-security multiversedeb-src http://security.ubuntu.com/ ubuntuprecision-security multiverse ##次の2行のコメントを解除して、Canonicalの##'部分からソフトウェアを追加しますner'リポジトリ。##このソフトウェアはUbuntuの一部ではありませんが、Canonicalと##それぞれのベンダーによってUbuntuユーザーへのサービスとして提供されています。#deb http://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu正確なパートナー#deb- src http://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu正確なパートナー##次の2行のコメントを解除して、Ubuntuの##'extras'リポジトリからソフトウェアを追加します。##このソフトウェアはUbuntuの一部ではありませんが、サードパーティによって提供されています##最新のソフトウェアを出荷したい開発者。#deb http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntuprecision main#deb-src http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu Acculate main |
次に実行します
apt-get update
aptパッケージデータベースを更新するには
apt-get upgrade
最新のアップデートをインストールします(ある場合)。更新の一部として新しいカーネルがインストールされていることがわかった場合は、後でシステムを再起動する必要があります。
再起動
9デフォルトのシェルを変更する
/ bin/shは/bin/ dashへのシンボリックリンクですが、/ bin/dashではなく/bin/bashが必要です。したがって、これを行います:
dpkg-reconfigure dash
デフォルトのシステムシェル(/ bin / sh)としてダッシュを使用しますか? <-いいえ
これを行わないと、ISPConfigのインストールが失敗します。
10AppArmorを無効にする
AppArmorは、拡張セキュリティを提供するセキュリティ拡張機能(SELinuxと同様)です。私の意見では、安全なシステムを構成するためにそれを必要とせず、通常、利点よりも多くの問題を引き起こします(一部のサービスが期待どおりに機能しなかったため、1週間のトラブルシューティングを行った後、それを考えてください。すべてが問題ないことを確認してください。AppArmorだけが問題を引き起こしていました)。したがって、無効にします(後でISPConfigをインストールする場合は必須です)。
次のように無効にできます:
/etc/init.d/apparmor stop
update-rc.d -f apparmor remove
apt-get remove apparmor apparmor-utils
11システム時計を同期する
システムクロックをNTPと同期することをお勧めします( n etwork t ime p rotocol)インターネット上のサーバー。実行するだけです
apt-get install ntp ntpdate
システム時刻は常に同期されます。
完璧なサーバー-Ubuntu12.04LTS(Apache2、BIND、Dovecot、ISPConfig 3)-4ページ
12 Postfix、Dovecot、MySQL、phpMyAdmin、rkhunter、binutilsをインストールします
Postfix、Dovecot、MySQL、rkhunter、binutilsを1つのコマンドでインストールできます:
apt-get install postfix postfix-mysql postfix-doc mysql-client mysql-server openssl getmail4 rkhunter binutils dovecot-imapd dovecot-pop3d dovecot-mysql dovecot-sieve sudo
次の質問があります:
MySQL「root」ユーザーの新しいパスワード:<-yourrootsqlpassword
MySQL「root」ユーザーの繰り返しパスワード:<-yourrootsqlpassword
メール構成の一般的なタイプ:<-インターネットサイト
システムメール名:<-server1.example.com
次に、PostfixでTLS / SSLと送信ポートを開きます:
vi /etc/postfix/master.cf
送信セクションとsmtpsセクションのコメントを解除します(不要なため、-o milter_macro_daemon_name =ORIGINATINGのままにします):
[...] subject inet n --- --- smtpd -o syslog_name =postfix / subject -o smtpd_tls_security_level =encrypt -o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable =yes- o smtpd_client_restrictions =permit_sasl_authenticated、reject#-o milter_macro_daemon_name =ORIGINATINGsmtps inet n --- --- smtpd -o syslog_name =postfix / smtps -o smtpd_tls_wrappermode =yes -o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable =...] |
その後、Postfixを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/postfix restart
MySQLがローカルホストだけでなくすべてのインターフェースでリッスンするようにしたいので、/ etc / mysql / my.cnfを編集して、bind-address =127.0.0.1:
の行をコメントアウトします。vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
[...]#スキップネットワークの代わりに、デフォルトでは、互換性が高く安全性が低くないローカルホストでのみリッスンするようになりました。 #bind-address =127.0.0.1 [...] |
次に、MySQLを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/mysql restart
次に、ネットワーキングが有効になっていることを確認します。実行
netstat -tap | grep mysql
出力は次のようになります。
example@unixlinux.online:〜#netstat -tap | grep mysql
tcp 0 0 *:mysql *:* LISTEN 21298 / mysqld
example@unixlinux.online:
13 Amavisd-new、SpamAssassin、およびClamavをインストールします
amavisd-new、SpamAssassin、およびClamAVをインストールするには、
を実行します。apt-get install amavisd-new spamassassin clamav clamav-daemon zoo unzip bzip2 arj nomarch lzop cabextract apt-listchanges libnet-ldap-perllibauthen-sasl-perlclamav-docsデーモンlibio-string-perllibio-socket-ssl- perl libnet-ident-perl zip libnet-dns-perlISPConfig 3のセットアップでは、SpamAssassinフィルターライブラリを内部的にロードするamavisdを使用するため、SpamAssassinを停止してRAMを解放できます。
/etc/init.d/spamassassin stop
update-rc.d -f spamassassin remove
14 Apache2、PHP5、phpMyAdmin、FCGI、suExec、Pear、およびmcryptをインストールします
Apache2、PHP5、phpMyAdmin、FCGI、suExec、Pear、およびmcryptは、次のようにインストールできます。
apt-get install apache2 apache2.2-common apache2-doc apache2-mpm-prefork apache2-utils libexpat1 ssl-cert libapache2-mod-php5 php5 php5-common php5-gd php5-mysql php5-imap phpmyadmin php5-cli php5-cgi libapache2-mod-fcgid apache2-suexec php-pear php-auth php5-curl php5-mcrypt mcrypt php5-imagick imagemagick libapache2-mod-suphp libruby libapache2-mod-ruby libapache2-mod-python libapache2-mod-perl2次の質問が表示されます:
自動的に再構成するWebサーバー:<-apache2
dbconfig-commonを使用してphpmyadminのデータベースを構成しますか? <-いいえ次に、次のコマンドを実行して、Apacheモジュールのsuexec、rewrite、ssl、actions、およびinclude(さらに、WebDAVを使用する場合はdav、dav_fs、およびauth_digest)を有効にします。
a2enmod suexecrewritesslアクションには次のものが含まれますa2enmod dav_fs dav auth_digestその後、Apacheを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/apache2再起動ISPConfigを介して作成されたWebサイトで拡張子.rbのRubyファイルをホストする場合は、/ etc/mime.typesのapplication/x-rubyrb行をコメントアウトする必要があります。
vi /etc/mime.types
[...]#application / x-ruby rb [...] |
(これは.rbファイルにのみ必要です。拡張子が.rbxのRubyファイルはそのまま使用できます。)
その後、Apacheを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/apache2再起動
14.1 Xcache
Xcacheは、PHP中間コードをキャッシュおよび最適化するための無料のオープンPHPオペコードキャッシャーです。これは、eAcceleratorやAPCなどの他のPHPオペコードキャッシャーに似ています。 PHPページを高速化するために、これらのいずれかをインストールすることを強くお勧めします。
Xcacheは次のようにインストールできます:
apt-get install php5-xcache
次にApacheを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/apache2再起動
14.2 PHP-FPM
今後のISPConfig3.0.5から、Apacheで使用するために選択できる追加のPHPモードPHP-FPMが追加されます。このPHPモードを使用する場合は、システムを今すぐ構成して、後でISPConfig 3.0.5にアップグレードするときにシステムが準備されるようにすることをお勧めします(この記事の執筆時点での最新のISPConfigバージョンはISPConfig 3.0です)。 .4.4)。
PHP-FPMをApacheで使用するには、mod_fastcgi Apacheモジュールが必要です(これをmod_fcgidと混同しないでください。これらは非常に似ていますが、PHP-FPMをmod_fcgidで使用することはできません)。 PHP-FPMとmod_fastcgiは次のようにインストールできます:
apt-get install libapache2-mod-fastcgi php5-fpm
モジュールを有効にして、Apacheを再起動してください:
a2enmodアクションfastcgiエイリアス
/etc/init.d/apache2restart
15Mailmanをインストール
バージョン3.0.4以降、ISPConfigではMailmanメーリングリストを管理(作成/変更/削除)することもできます。この機能を利用する場合は、次のようにMailmanをインストールします。
apt-get install mailman
少なくとも1つの言語を選択してください。例:
サポートする言語:<-en(英語)
Mailmanを開始する前に、mailmanという最初のメーリングリストを作成する必要があります。
newlist mailman
example@unixlinux.online:〜#newlist mailman
リストを実行している人のメールアドレスを入力します:<-admin email address、e.g. example@unixlinux.online
最初のメールマンパスワード:<-メールマンリストの管理者パスワード
メールリストの作成を完了するには、/ etc / aliases(または
同等の)ファイルを編集する必要があります次の行を追加し、場合によっては
「newaliases」プログラムを実行します。
## mailman mailing list
mailman: "| / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman post mailman "
mailman-admin:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman admin mailman "
mailman-bounces:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman bounces mailman "
mailman-confirm: "| / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman confirm mailman"
mailman-join: "| / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman join mailman"
mailman -leave: "| / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman Leave mailman"
mailman-owner: "| / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman owner mailman"
mailman-request: " | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman request mailman "
mailman-subscribe:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman subscribe mailm an "
mailman-unsubscribe:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman unsubscribe mailman "
Enterキーを押して、mailmanの所有者に通知します... <-ENTER
example@unixlinux.online:〜#
後で/etc/aliasesを開きます...
vi / etc / aliases
...そして次の行を追加します:
[...] ## mailman mailing listmailman: "| / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman post mailman" mailman-admin: " | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman admin mailman "mailman-bounces:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman bounces mailman "mailman-confirm:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail /mailmanconfirm mailman "mailman-join:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman join mailman "mailman-leave:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman Leave mailman "mailman-owner:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman owner mailman "mailman-request:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman request mailman "mailman-subscribe:" | / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman subscribe mailman "mailman-unsubscribe :"| / var / lib / mailman / mail / mailman unsubscribe mailman" |
実行
newaliases
その後、Postfixを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/postfix restart
最後に、MailmanApache構成を有効にする必要があります。
ln -s /etc/mailman/apache.conf /etc/apache2/conf.d/mailman.conf
これにより、すべてのApachevhostのエイリアス/cgi-bin / mailman /が定義されます。つまり、http://
http://
その後、Apacheを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/apache2再起動
次に、Mailmanデーモンを起動します:
/etc/init.d/mailman start
完璧なサーバー-Ubuntu12.04LTS(Apache2、BIND、Dovecot、ISPConfig 3)-5ページ
16PureFTPdとクォータのインストール
PureFTPdとquotaは、次のコマンドでインストールできます:
apt-get install pure-ftpd-common pure-ftpd-mysqlquotaquotatool
ファイル/etc/ default / pure-ftpd-common ...
を編集しますvi / etc / default / pure-ftpd-common
...そして、開始モードがスタンドアロンに設定されていることを確認し、VIRTUALCHROOT =trueを設定します:
[...] STANDALONE_OR_INETD =Standalone [...] VIRTUALCHROOT =true [...] |
次に、FTPおよびTLSセッションを許可するようにPureFTPdを構成します。 FTPは、すべてのパスワードとすべてのデータがクリアテキストで転送されるため、非常に安全でないプロトコルです。 TLSを使用することで、通信全体を暗号化できるため、FTPの安全性が大幅に向上します。
FTPおよびTLSセッションを許可する場合は、
を実行します。echo 1> / etc / pure-ftpd / conf / TLS
TLSを使用するには、SSL証明書を作成する必要があります。 / etc / ssl / private /に作成するので、最初にそのディレクトリを作成します:
mkdir -p / etc / ssl / private /
その後、次のようにSSL証明書を生成できます。
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 7300 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem -out /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
国名(2文字のコード)[AU]:<-国名を入力します(例:「DE」)。
州名または州名(フルネーム)[一部の州]:<-州を入力しますまたは州名。
地域名(例:市)[]:<-市区町村を入力してください。
組織名(例:会社)[Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:<-組織名を入力してください(例:会社名)
組織単位名(例:セクション)[]:<-組織単位名(例:「IT部門」)を入力します。
一般名(例:あなたの名前)[]:<-システムの完全修飾ドメイン名を入力します(例: "server1.example.com")。
メールアドレス[]:<-メールアドレスを入力します。
SSL証明書の権限を変更します:
chmod 600 /etc/ssl/private/pure-ftpd.pem
次に、PureFTPdを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/pure-ftpd-mysql restart
/ etc/fstabを編集します。私の場合は次のようになります(マウントポイントのあるパーティションに、usrjquota =quote.user、grpjquota =quote.group、jqfmt =vfsv0を追加しました/):
vi / etc / fstab
#/ etc / fstab:静的ファイルシステム情報。##「blkid」を使用して、#デバイスのユニバーサル一意識別子を出力します。これは、ディスクが追加および削除された場合でも機能するデバイスに名前を付けるためのより堅牢な方法として、UUID=とともに使用できます。 fstab(5)を参照してください。##<ファイルシステム><マウントポイント><タイプ><オプション><ダンプ><パス>proc / proc proc nodev、noexec、nosuid 0 0 / dev / mapper / server1-root/ext4エラー=remount-ro、usrjquota =quote.user、grpjquota =quote.group、jqfmt =vfsv0 0 1#/bootはインストール中に/dev/sda1にありましたUUID=4b58d345-1c55-4ac5-940e-7245938656a6 / boot ext2 defaults 0 2 / dev / mapper / server1-swap_1 none swap sw 0 0 / dev / fd0 / media / floppy0 auto rw、user、noauto、exec、utf8 0 0 |
クォータを有効にするには、次のコマンドを実行します。
mount -o remount /
quotecheck -avugm
quotaon-avug
17BINDDNSサーバーのインストール
BINDは次のようにインストールできます:
apt-get install bind9 dnsutils
18 Vlogger、Webalizer、およびAWstatsをインストールします
Vlogger、webalizer、AWstatsは次のようにインストールできます:
apt-get install vlogger webalizer awstats geoip-database libclass-dbi-mysql-perl
その後、/ etc / cron.d/awstatsを開きます...
vi /etc/cron.d/awstats
...そしてそのファイルのすべてをコメントアウトします:
#MAILTO =root#* / 10 * * * * www-data [-x /usr/share/awstats/tools/update.sh] &&/usr/share/awstats/tools/update.sh#静的レポートを生成します:#10 03 * * * www-data [-x /usr/share/awstats/tools/buildstatic.sh] &&/usr/share/awstats /tools/buildstatic.sh |
19Jailkitをインストールする
Jailkitは、SSHユーザーをchrootする場合にのみ必要です。次のようにインストールできます(重要:JailkitはISPConfigの前にインストールする必要があります-後でインストールすることはできません!):
apt-get install build-essential autoconf automake1.9 libtool flex bison debhelper binutils-gold
cd / tmp
wget http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/jailkit-2.14.tar.gz
tar xvfz jailkit-2.14.tar.gz
cd jailkit- 2.14
./debian/rules binary
これで、次のようにJailkit.debパッケージをインストールできます。
cd ..
dpkg -i jailkit_2.14-1_*。deb
rm -rf jailkit-2.14 *
20fail2banをインストール
これはオプションですが、ISPConfigモニターがログを表示しようとするため、推奨されます:
apt-get install fail2ban
fail2banでPureFTPdとDovecotを監視するには、ファイル/etc/fail2ban/jail.local:
を作成します。vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
[pureftpd] enabled =trueport =ftpfilter =pureftpdlogpath =/ var / log / syslogmaxretry =3 [dovecot-pop3imap] enabled =truefilter =dovecot-pop3imapaction =iptables-multiport [name =dovecot-pop3imap、port ="pop3、pop3s、imap、imaps"、protocol =tcp] logpath =/var/log/mail.logmaxretry =5 |
次に、次の2つのフィルターファイルを作成します。
vi /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/pureftpd.conf
[Definition] failregex=。*pure-ftpd:\(。* @ |
vi /etc/fail2ban/filter.d/dovecot-pop3imap.conf
[Definition] failregex =(?:pop3-login | imap-login):。*(?:認証に失敗しました|ログインを中止しました\(認証に失敗しました|ログインの中止\(無効を使用しようとしました|切断されました\(認証に失敗しました|ログインの中止\(\ d +認証の試行))* rip =(?P |
その後、fail2banを再起動します:
/etc/init.d/fail2ban再起動
完璧なサーバー-Ubuntu12.04LTS(Apache2、BIND、Dovecot、ISPConfig 3)-6ページ
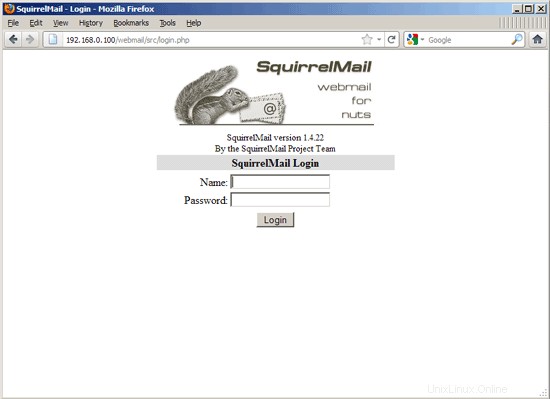
21SquirrelMailをインストールする
SquirrelMailウェブメールクライアントをインストールするには、
を実行しますapt-get install squirrelmail
次に、SquirrelMailを設定します:
squirrelmail-configure
Dovecot-IMAP / -POP3を使用していることをSquirrelMailに通知する必要があります:
SquirrelMailの構成:読み取り:config.php(1.4.0)
--------------------------------- ------------------------
メインメニュー-
1.組織の設定
2.サーバーの設定
3.フォルダのデフォルト
4.一般的なオプション
5.テーマ
6.アドレスブック
7.今日のメッセージ(MOTD)
8.プラグイン
9.データベース
10.言語
D.特定のIMAPサーバー用に事前定義された設定を設定します
C色をオンにします
S保存data
Q Quit
Command>> <-D
SquirrelMail Configuration:Read:config.php
---- -------------------------------------------------- ---
SquirrelMailを構築している間に、他のサーバーではうまく機能しない一部のサーバーでより効果的に機能する
いくつかの設定を発見しました。 IMAPサーバーを選択した場合、このオプションにより、そのサーバーに事前定義された設定が
設定されます。
引き続き、すべてを確認する必要があることに注意してください。
正しい。これによってすべてが変わるわけではありません。
これが変更される設定はごくわずかです。
IMAPサーバーを選択してください:
bincimap =BincIMAPサーバー
courier=CourierIMAPサーバー
cyrus =CyrusIMAPサーバー
dovecot=DovecotSecureIMAPサーバー
exchange=Microsoft Exchange IMAP server
hmailserver =hMailServer
hmailserver =hMailServer
/ 32
uw=ワシントン大学のIMAPサーバー
gmail=Googleメール(Gmail)アカウントへのIMAPアクセス
-dovecot
SquirrelMailの構成:読み取り:config.php
----------------------- ----------------------------------
SquirrelMailを構築している間に、いくつかの<を発見しました。 br />一部のサーバーではうまく機能する設定で、他のサーバーではうまく機能しない
。 IMAPサーバーを選択した場合、このオプションにより、そのサーバーに事前定義された設定が
設定されます。
引き続き、すべてを確認する必要があることに注意してください。
正しい。これによってすべてが変わるわけではありません。
これが変更される設定はごくわずかです。
IMAPサーバーを選択してください:
bincimap =BincIMAPサーバー
courier=CourierIMAPサーバー
cyrus =CyrusIMAPサーバー
dovecot=DovecotSecureIMAPサーバー
exchange=Microsoft Exchange IMAP server
hmailserver =hMailServer
hmailserver =hMailServer
/32
uw = University of Washington's IMAP server
gmail = IMAP access to Google mail (Gmail) accounts
quit = Do not change anything
Command >> dovecot
imap_server_type = dovecot
default_folder_prefix =
trash_folder = Trash
sent_folder = Sent
draft_folder = Drafts
show_prefix_option = false
default_sub_of_inbox = false
show_co ntain_subfolders_option = false
optional_delimiter = detect
delete_folder = false
Press any key to continue... <-- press a key
SquirrelMail Configuration : Read: config.php (1.4.0)
---------------------------------------------------------
Main Menu --
1. Organization Preferences
2. Server Settings
3. Folder Defaults
4. General Options
5. Themes
6. Address Books
7. Message of the Day (MOTD)
8. Plugins
9. Database
10. Languages
D. Set pre-defined settings for specific IMAP servers
C Turn color on
S Save data
Q Quit
Command >> <-- S
SquirrelMail Configuration : Read: config.php (1.4.0)
---------------------------------------------------------
Main Menu --
1. Organization Preferences
2. Server Settings
3. Folder Defaults
4 . General Options
5. Themes
6. Address Books
7. Message of the Day (MOTD)
8. Plugins
9. Database
10. Languages
D. Set pre-defined settings for specific IMAP servers
C Turn color on
S Save data
Q Quit
Command >> <-- Q
Now we will configure SquirrelMail so that you can use it from within your web sites (created through ISPConfig) by using the /squirrelmail or /webmail aliases. So if your website is www.example.com, you will be able to access SquirrelMail using www.example.com/squirrelmail or www.example.com/webmail.
SquirrelMail's Apache configuration is in the file /etc/squirrelmail/apache.conf, but this file isn't loaded by Apache because it is not in the /etc/apache2/conf.d/ directory. Therefore we create a symlink called squirrelmail.conf in the /etc/apache2/conf.d/ directory that points to /etc/squirrelmail/apache.conf and reload Apache afterwards:
cd /etc/apache2/conf.d/
ln -s ../../squirrelmail/apache.conf squirrelmail.conf
/etc/init.d/apache2 reload
Now open /etc/apache2/conf.d/squirrelmail.conf...
vi /etc/apache2/conf.d/squirrelmail.conf
... and add the following lines to the
[...] |
Create the directory /var/lib/squirrelmail/tmp...
mkdir /var/lib/squirrelmail/tmp
... and make it owned by the user www-data:
chown www-data /var/lib/squirrelmail/tmp
Reload Apache again:
/etc/init.d/apache2 reload
That's it already - /etc/apache2/conf.d/squirrelmail.conf defines an alias called /squirrelmail that points to SquirrelMail's installation directory /usr/share/squirrelmail.
You can now access SquirrelMail from your web site as follows:
http://192.168.0.100/squirrelmail
http://www.example.com/squirrelmail
You can also access it from the ISPConfig control panel vhost (after you have installed ISPConfig, see the next chapter) as follows (this doesn't need any configuration in ISPConfig):
http://server1.example.com:8080/squirrelmail
If you'd like to use the alias /webmail instead of /squirrelmail, simply open /etc/apache2/conf.d/squirrelmail.conf...
vi /etc/apache2/conf.d/squirrelmail.conf
... and add the line Alias /webmail /usr/share/squirrelmail:
Alias /squirrelmail /usr/share/squirrelmailAlias /webmail /usr/share/squirrelmail[...] |
Then reload Apache:
/etc/init.d/apache2 reload
Now you can access Squirrelmail as follows:
http://192.168.0.100/webmail
http://www.example.com/webmail
http://server1.example.com:8080/webmail (after you have installed ISPConfig, see the next chapter)
If you'd like to define a vhost like webmail.example.com where your users can access SquirrelMail, you'd have to add the following vhost configuration to /etc/apache2/conf.d/squirrelmail.conf:
vi /etc/apache2/conf.d/squirrelmail.conf
[...] |
Make sure you replace 1.2.3.4 with the correct IP address of your server. Of course, there must be a DNS record for webmail.example.com that points to the IP address that you use in the vhost configuration. Also make sure that the vhost webmail.example.com does not exist in ISPConfig (otherwise both vhosts will interfere with each other!).
Now reload Apache...
/etc/init.d/apache2 reload
... and you can access SquirrelMail under http://webmail.example.com!
The Perfect Server - Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (Apache2, BIND, Dovecot, ISPConfig 3) - Page 7
22 Install ISPConfig 3
To install ISPConfig 3 from the latest released version, do this:
cd /tmp
wget http://www.ispconfig.org/downloads/ISPConfig-3-stable.tar.gz
tar xfz ISPConfig-3-stable.tar.gz
cd ispconfig3_install/install/
The next step is to run
php -q install.php
This will start the ISPConfig 3 installer. The installer will configure all services like Postfix, Dovecot, etc. for you. A manual setup as required for ISPConfig 2 (perfect setup guides) is not necessary.
example@unixlinux.online:/tmp/ispconfig3_install/install# php -q install.php
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
_____ ___________ _____ __ _ ____
|_ _/ ___| ___ \ / __ \ / _(_) /__ \
| | \ `--.| |_/ / | / \/ ___ _ __ | |_ _ __ _ _/ /
| | `--. \ __/ | | / _ \| '_ \| _| |/ _` | |_ |
_| |_/\__/ / | | \__/\ (_) | | | | | | | (_| | ___\ \
\___/\____/\_| \____/\___/|_| |_|_| |_|\__, | \____/
__/ |
|___/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
>> Initial configuration
Operating System: Debian or compatible, unknown version.
Following will be a few questions for primary configuration so be careful.
Default values are in [brackets] and can be accepted with
Tap in "quit" (without the quotes) to stop the installer.
Select language (en,de) [en]: <-- ENTER
Installation mode (standard,expert) [standard]: <-- ENTER
Full qualified hostname (FQDN) of the server, eg server1.domain.tld [server1.example.com]: <-- ENTER
MySQL server hostname [localhost]: <-- ENTER
MySQL root username [root]: <-- ENTER
MySQL root password []: <-- yourrootsqlpassword
MySQL database to create [dbispconfig]: <-- ENTER
MySQL charset [utf8]: <-- ENTER
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
...........+++
.....................+++
writing new private key to 'smtpd.key'
-----
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]: <-- ENTER
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]: <-- ENTER
Locality Name (eg, city) []: <-- ENTER
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]: <-- ENTER
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: <-- ENTER
C ommon Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []: <-- ENTER
Email Address []: <-- ENTER
Configuring Jailkit
Configuring Dovecot
Configuring Spamassassin
Configuring Amavisd
Configuring Getmail
Configuring Pureftpd
Configuring BIND
Configuring Apache
Configuring Vlogger
Configuring Apps vhost
Configuring Bastille Firewall
Configuring Fail2ban
Installing ISPConfig
ISPConfig Port [8080]: <-- ENTER
Do you want a secure (SSL) connection to the ISPConfig web interface (y,n) [y]: <-- ENTER
Generating RSA private key, 4096 bit long modulus
.......++
.........................................................++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some b lank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]: <-- ENTER
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]: <-- ENTER
Locality Name (eg, city) []: <-- ENTER
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]: <-- ENTER
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: <-- ENTER
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []: <-- ENTER
Email Address []: <-- ENTER
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []: <-- ENTER
An optional company name []: <-- ENTER
writing RSA key
Configuring DBServer
Installing ISPConfig crontab
no crontab for root
no crontab for getmail
Restarting services ...
Rather than invoking init scripts through /etc/init.d, use the service(8)
utility, e.g. service mysql restart
Since the script you are attempting to invoke has been converted to an
Upstart job, you may also use the stop(8) and then start(8) utilities,
e.g. stop mysql ; start mysql. The restart(8) utility is also available.
mysql stop/waiting
mysql start/running, process 2543
* Stopping Postfix Mail Transport Agent postfix
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
...done.
* Starting Postfix Mail Transport Agent postfix
postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_ bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postcon f: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
/usr/sbin/postconf: warning: /etc/postfix/master.cf: unused parameter: smtpd_bind_address=127.0.0.1
...done.
Stopping amavisd: (not running).
The amavisd daemon is already running, PID: [1126]
Starting amavisd: (failed).
* Stopping ClamAV daemon clamd
...done.
* Starting ClamAV daemon clamd
...done.
Rather than invoking init scripts through /etc/init.d, use the service(8)
utility, e.g. service dovecot restart
Since the script you are attempting to invoke has been converted to an
Upstart job, you may also use the stop(8) and then start(8) utilities,
e.g. stop dovecot ; start dovecot. The restart(8) utility is also available.
dovecot stop/waiting
dovecot start/running, process 3668
* Restarting Mailman master qrunner mailmanctl
* Waiting...
...done.
...done.
* Restarting web server apache2
... waiting . ...done.
Restarting ftp server: Running: /usr/sbin/pure-ftpd-mysql-virtualchroot -l mysql:/etc/pure-ftpd/db/mysql.conf -l pam -E -H -Y 1 -O clf:/var/log/pure-ftpd/transfer.log -8 UTF-8 -b -D -A -u 1000 -B
Installation completed.
example@unixlinux.online:/tmp/ispconfig3_install/install#
The installer automatically configures all underlying services, so no manual configuration is needed.
You now also have the possibility to let the installer create an SSL vhost for the ISPConfig control panel, so that ISPConfig can be accessed using https:// instead of http://. To achieve this, just press ENTER when you see this question:Do you want a secure (SSL) connection to the ISPConfig web interface (y,n) [y]:.
Afterwards you can access ISPConfig 3 under http(s)://server1.example.com:8080/ or http(s)://192.168.0.100:8080/ ( http or https depends on what you chose during installation). Log in with the username admin and the password admin (you should change the default password after your first login):
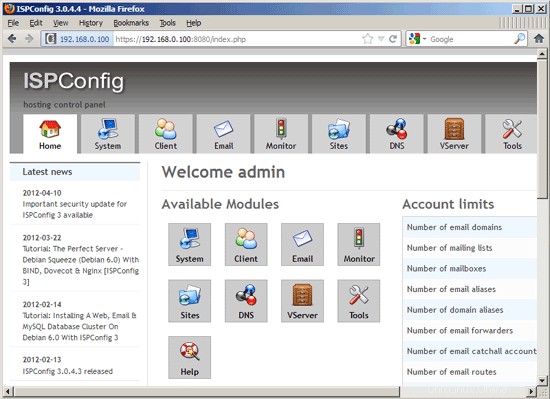
The system is now ready to be used.
22.1 ISPConfig 3 Manual
In order to learn how to use ISPConfig 3, I strongly recommend to download the ISPConfig 3 Manual.
On more than 300 pages, it covers the concept behind ISPConfig (admin, resellers, clients), explains how to install and update ISPConfig 3, includes a reference for all forms and form fields in ISPConfig together with examples of valid inputs, and provides tutorials for the most common tasks in ISPConfig 3. It also lines out how to make your server more secure and comes with a troubleshooting section at the end.
22.2 ISPConfig Monitor App For Android
ISPConfig Monitor Appを使用すると、サーバーのステータスを確認し、すべてのサービスが期待どおりに実行されているかどうかを確認できます。 TCPおよびUDPポートを確認し、サーバーにpingを実行できます。さらに、このアプリを使用して、ISPConfigがインストールされているサーバーに詳細を要求できます(ISPConfigモニターアプリをサポートするインストール済みのISPConfig3の最小バージョンは3.0.3.3です! );これらの詳細には、ISPConfigコントロールパネルのモニターモジュールから知っているすべてのもの(サービス、メールとシステムのログ、メールキュー、CPUとメモリの情報、ディスク使用量、クォータ、OSの詳細、RKHunterログなど)が含まれます。 、ISPConfigはマルチサーバー対応であるため、ISPConfigマスターサーバーから制御されているすべてのサーバーを確認できます。
ダウンロードと使用方法については、http://www.ispconfig.org/ispconfig-3/ispconfig-monitor-app-for-android/にアクセスしてください。
23 Additional Notes
23.1 OpenVZ
If the Ubuntu server that you've just set up in this tutorial is an OpenVZ container (virtual machine), you should do this on the host system (I'm assuming that the ID of the OpenVZ container is 101 - replace it with the correct VPSID on your system):
VPSID=101
for CAP in CHOWN DAC_READ_SEARCH SETGID SETUID NET_BIND_SERVICE NET_ADMIN SYS_CHROOT SYS_NICE CHOWN DAC_READ_SEARCH SETGID SETUID NET_BIND_SERVICE NET_ADMIN SYS_CHROOT SYS_NICE
do
vzctl set $VPSID --capability ${CAP}:on --save
done
24 Links
- Ubuntu:http://www.ubuntu.com/
- ISPConfig:http://www.ispconfig.org/
About The Author

Falko Timme is the owner of  Timme Hosting (ultra-fast nginx web hosting). He is the lead maintainer of HowtoForge (since 2005) and one of the core developers of ISPConfig (since 2000). He has also contributed to the O'Reilly book "Linux System Administration".
Timme Hosting (ultra-fast nginx web hosting). He is the lead maintainer of HowtoForge (since 2005) and one of the core developers of ISPConfig (since 2000). He has also contributed to the O'Reilly book "Linux System Administration".