
このチュートリアルでは、Ubuntu 18.04 LTSにNtopngをインストールする方法を紹介します。知らなかった方のために、Ntopngは、さまざまなモニターを探している場合に比較的便利なツールです。サーバー上のネットワークプロトコル。さまざまなプロトコル、トラフィックバリアント、およびはい、複数の時間枠にわたる帯域幅を監視するための一連のツールを提供します。Ntopngはlibpcapに基づいており、すべてのユーザーで仮想的に実行できるようにポータブルな方法で記述されています。 Unixプラットフォーム、Mac OS、およびWin32でも。
この記事は、少なくともLinuxの基本的な知識があり、シェルの使用方法を知っていること、そして最も重要なこととして、サイトを独自のVPSでホストしていることを前提としています。インストールは非常に簡単で、ルートアカウントで実行されていますが、そうでない場合は、'sudoを追加する必要があります。 ‘ルート権限を取得するコマンドに。 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS(Bionic Beaver)サーバーにNtopngを段階的にインストールする方法を紹介します。
前提条件
- 次のオペレーティングシステムのいずれかを実行しているサーバー:Ubuntu 18.04、およびLinuxMintなどの他のDebianベースのディストリビューション。
- 潜在的な問題を防ぐために、OSの新規インストールを使用することをお勧めします。
- サーバーへのSSHアクセス(またはデスクトップを使用している場合はターミナルを開く)。
non-root sudo userまたはroot userへのアクセス 。non-root sudo userとして行動することをお勧めします ただし、ルートとして機能するときに注意しないと、システムに害を及ぼす可能性があるためです。
Ubuntu 18.04 LTSBionicBeaverにNtopngをインストール
手順1.まず、次のapt-getを実行して、すべてのシステムパッケージが最新であることを確認します。 ターミナルのコマンド。
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
Ntopngをインストールするには、サーバーのrootユーザーとして次のコマンドを実行します。
wget http://apt.ntop.org/18.04/all/apt-ntop.deb dpkg -i apt-ntop.deb
次に、実行します:
apt-get update apt-get install pfring-dkms nprobe ntopng n2disk cento
手順3.Ntopngを設定します。
Ntopng構成ファイルを作成します。この記事では、nanoをテキストエディターとして使用します。お気に入りのテキストエディターを使用して、Ntopng構成ファイルを作成できます。
>sudo nano /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf
# /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf # # The configuration file is similar to the command line, with the exception that an equal # sign '=' must be used between key and value. Example: -i=p1p2 or --interface=p1p2 For # options with no value (e.g. -v) the equal is also necessary. Example: "-v=" must be used. # # # -G|--pid-path # Specifies the path where the PID (process ID) is saved. # -G=/var/tmp/ntopng.pid # # -e|--daemon # This parameter causes ntop to become a daemon, i.e. a task which runs in the background # without connection to a specific terminal. To use ntop other than as a casual monitoring # tool, you probably will want to use this option. # -e= # # -i|--interface # Specifies the network interface or collector endpoint to be used by ntopng for network # monitoring. On Unix you can specify both the interface name (e.g. lo) or the numeric # interface id as shown by ntopng -h. On Windows you must use the interface number instead. # Note that you can specify -i multiple times in order to instruct ntopng to create multi‐ # ple interfaces. # -i=1 # # -w|--http-port # Sets the HTTP port of the embedded web server. # -w=3000 # # -m|--local-networks # ntopng determines the ip addresses and netmasks for each active interface. Any traffic on # those networks is considered local. This parameter allows the user to define additional # networks and subnetworks whose traffic is also considered local in ntopng reports. All # other hosts are considered remote. If not specified the default is set to 192.168.1.0/24. # # Commas separate multiple network values. Both netmask and CIDR notation may be used, # even mixed together, for instance "131.114.21.0/24,10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0". # -m=192.168.1.0/24 # # -n|--dns-mode # Sets the DNS address resolution mode: 0 - Decode DNS responses and resolve only local # (-m) numeric IPs 1 - Decode DNS responses and resolve all numeric IPs 2 - Decode DNS # responses and don't resolve numeric IPs 3 - Don't decode DNS responses and don't resolve # -n=1 # # -S|--sticky-hosts # ntopng periodically purges idle hosts. With this option you can modify this behaviour by # telling ntopng not to purge the hosts specified by -S. This parameter requires an argu‐ # ment that can be "all" (Keep all hosts in memory), "local" (Keep only local hosts), # "remote" (Keep only remote hosts), "none" (Flush hosts when idle). # -S= # # -d|--data-dir # Specifies the data directory (it must be writable). Default directory is ./data # -d=/var/tmp/ntopng # # -q|--disable-autologout # Disable web interface logout for inactivity. # -q=
ntopng.startファイルを作成します:
sudo nano /etc/ntopng/ntopng.start ##Add this line## --local-networks "192.168.0.0/24" ## give your local IP Ranges here. --interface 1
使用可能なすべてのインターフェースとオプションを表示するには、ntopng -hを使用します オプション:
sudo ntopng -h
Ntopngサーバーデーモンを起動します:
systemctl start ntopng.service systemctl start redis-server.service
ステップ4.Ntopngへのアクセス。
これで、http://your-server-ip-address:3000と入力して、Ntopngアプリケーションをテストできます。 。 Ntopngログインページが表示されます。初めて、ユーザー「admin」とパスワード「admin」を使用できるようになりました。
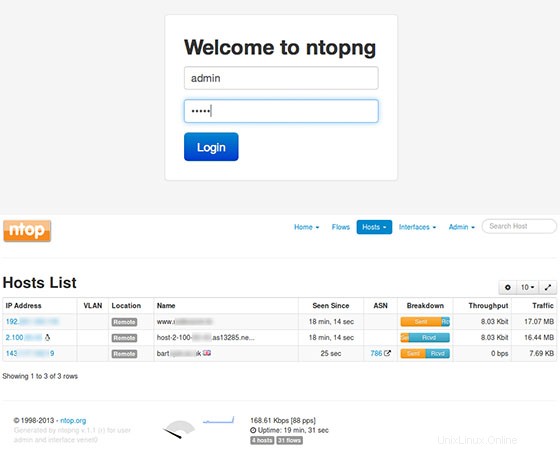
おめでとうございます。Ntopngが正常にインストールされました。このチュートリアルを使用して、Ubuntu 18.04 LTSBionicBeaverシステムにNtopng高速Webベースのトラフィック分析とフロー収集をインストールしていただきありがとうございます。役立つ情報については、Ntopngの公式Webサイトを確認することをお勧めします。