
Let’s Encryptは、Internet Security Research Group(ISRG)によって開発された、無料の自動化されたオープンな認証局です。 Let’s Encryptによって発行された証明書は、発行日から90日間有効であり、今日のすべての主要なブラウザによって信頼されています。
このチュートリアルでは、ApacheをWebサーバーとして実行しているCentOS7サーバーに無料のLet'sEncryptSSL証明書をインストールするために必要な手順について説明します。 certbotユーティリティを使用して、Let’sEncrypt証明書を取得および更新します。
前提条件#
このチュートリアルを続行する前に、次の前提条件を満たしていることを確認してください。
- パブリックサーバーのIPを指すドメイン名を使用します。
example.comを使用します 。 - Apacheがサーバーにインストールされて実行されています。
- ドメインにApache仮想ホストを用意します。
- ポート80と443はファイアウォールで開いています。
SSL暗号化Webサーバーに必要な次のパッケージをインストールします。
yum install mod_ssl opensslCertbot#をインストールします
Certbotは、Let’s EncryptからSSL証明書を取得し、サーバーでHTTPSを自動有効化するプロセスを簡素化するツールです。
certbotパッケージは、EPELからインストールできます。 EPELリポジトリがシステムにインストールされていない場合は、次のコマンドを使用してインストールできます。
sudo yum install epel-releaseEPELリポジトリを有効にしたら、次のように入力してcertbotパッケージをインストールします。
sudo yum install certbot強力なDh(Diffie-Hellman)グループ番号を生成します#
Diffie-Hellman鍵交換(DH)は、セキュリティで保護されていない通信チャネルを介して暗号化キーを安全に交換する方法です。セキュリティを強化するために、2048ビットのDHパラメータの新しいセットを生成します。
sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 2048Let’s EncryptのSSL証明書の取得#
ドメインのSSL証明書を取得するには、${webroot-path}/.well-known/acme-challenge ディレクトリ。 Let’s Encryptサーバーは、一時ファイルに対してHTTPリクエストを送信して、リクエストされたドメインがcertbotが実行されているサーバーに解決されることを検証します。
より簡単にするために、.well-known/acme-challengeのすべてのHTTPリクエストをマッピングします。 単一のディレクトリに、/var/lib/letsencrypt 。
次のコマンドを実行してディレクトリを作成し、Apacheサーバーで書き込み可能にします。
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/letsencrypt/.well-knownsudo chgrp apache /var/lib/letsencryptsudo chmod g+s /var/lib/letsencrypt
コードの重複を避けるために、次の2つの構成スニペットを作成します。
/etc/httpd/conf.d/letsencrypt.confAlias /.well-known/acme-challenge/ "/var/lib/letsencrypt/.well-known/acme-challenge/"
<Directory "/var/lib/letsencrypt/">
AllowOverride None
Options MultiViews Indexes SymLinksIfOwnerMatch IncludesNoExec
Require method GET POST OPTIONS
</Directory>
SSLCipherSuite EECDH+AESGCM:EDH+AESGCM:AES256+EECDH:AES256+EDH
SSLProtocol All -SSLv2 -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1
SSLHonorCipherOrder On
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubDomains; preload"
Header always set X-Frame-Options SAMEORIGIN
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options nosniff
# Requires Apache >= 2.4
SSLCompression off
SSLUseStapling on
SSLStaplingCache "shmcb:logs/stapling-cache(150000)"
# Requires Apache >= 2.4.11
SSLSessionTickets Off
上記のスニペットには、推奨されるチッパーが含まれており、OCSPステープリング、HTTP Strict Transport Security(HSTS)を有効にし、セキュリティに重点を置いたHTTPヘッダーをいくつか適用しています。
変更を有効にするためにApache構成を再ロードします:
sudo systemctl reload httpdこれで、webrootプラグインを使用してCertbotツールを実行し、次のように入力してSSL証明書ファイルを取得できます。
sudo certbot certonly --agree-tos --email admin@example.com --webroot -w /var/lib/letsencrypt/ -d example.com -d www.example.comSSL証明書が正常に取得されると、certbotは次のメッセージを出力します。
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2018-12-07. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot
again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run
"certbot renew"
- If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
CentOS 7には、SSLOpenSSLConfCmdが含まれていないApacheバージョン2.4.6が付属しています。 指令。このディレクティブは、Apache 2.4.8以降でのみ使用可能であり、Diffie–Hellman鍵交換(DH)などのOpenSSLパラメーターの構成に使用されます。
Let’sEncryptSSL証明書と生成されたDHファイルを使用して新しい結合ファイルを作成する必要があります。これを行うには、次のように入力します:
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/cert.pem /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem >/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/cert.dh.pemすべての設定が完了したので、ドメイン仮想ホストの構成を次のように編集します。
/etc/httpd/conf.d/example.com.conf<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
Redirect permanent / https://example.com/
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
<If "%{HTTP_HOST} == 'www.example.com'">
Redirect permanent / https://example.com/
</If>
DocumentRoot /var/www/example.com/public_html
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/example.com-error.log
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/example.com-access.log combined
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/cert.dh.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/chain.pem
# Other Apache Configuration
</VirtualHost>
上記の構成では、HTTPSを強制し、wwwバージョンから非wwwバージョンにリダイレクトしています。必要に応じて構成を自由に調整してください。
変更を有効にするには、Apacheサービスを再起動します。
sudo systemctl restart httpd
これで、https://を使用してWebサイトを開くことができます 緑色の鍵のアイコンが表示されます。
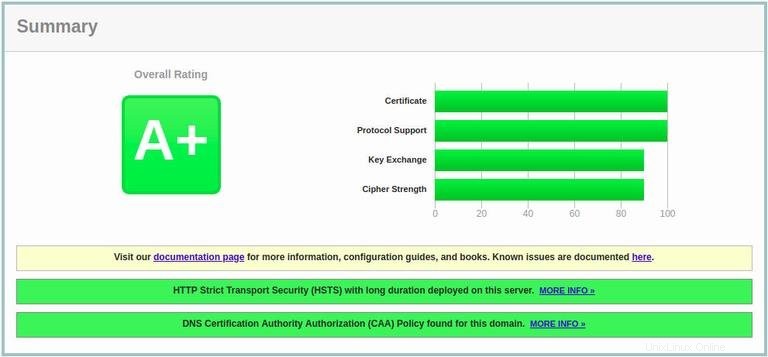
SSL Labsサーバーテストを使用してドメインをテストすると、以下に示すようにA+グレードを取得します。
自動更新Let’s Encrypt SSL証明書#
Let'sEncryptの証明書は90日間有効です。有効期限が切れる前に証明書を自動的に更新するために、1日に2回実行され、有効期限が切れる30日前に証明書を自動的に更新するcronジョブを作成します。
crontabを実行します 証明書を更新する新しいcronジョブを作成し、DHキーを含む新しい結合ファイルを作成し、apacheを再起動するコマンド:
sudo crontab -e0 */12 * * * root test -x /usr/bin/certbot -a \! -d /run/systemd/system && perl -e 'sleep int(rand(3600))' && certbot -q renew --renew-hook "systemctl reload httpd"
ファイルを保存して閉じます。
更新プロセスをテストするには、certbotコマンドに続けて--dry-runを使用できます。 スイッチ:
sudo certbot renew --dry-runエラーがない場合は、更新プロセスが成功したことを意味します。