Gitは、コードの変更を追跡するために使用できる無料のオープンソースバージョン管理システムです。 Gitを使用すると、同じアプリケーション用に多数のリポジトリを作成し、それらのファイルの作業を複数の人の間で調整できます。これは主に、ソフトウェア開発のソースコード管理に使用されます。
この記事では、Ubuntu 18.04 LTS(Bionic Beaver)にNginxを使用してHTTPGitサーバーをインストールする方法を学習します。
要件
- システムにインストールされている新しいUbuntu18.04サーバー。
- root権限を持つSudoユーザー。
- サーバーに静的IPアドレスが設定されています。このチュートリアルでは、IP192.168.1.100を使用します。
1はじめに
開始する前に、システムを最新の安定バージョンで更新する必要があります。
これを行うには、次のコマンドを実行します。
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get upgrade -y
システムが更新されたら、システムを再起動し、sudoユーザーでログインします。
2必要なパッケージをインストールする
まず、nginx、git、nano、fcgiwrapなどの必要なパッケージをシステムにインストールする必要があります。次のコマンドを実行して、それらすべてをインストールできます。
sudo apt-get install nginx git nano fcgiwrap apache2-utils -y
必要なパッケージがすべてインストールされたら、Gitリポジトリ用のディレクトリを作成する必要があります。これを行うには、次のコマンドを実行します。
sudo mkdir /var/www/html/git
次に、Gitディレクトリに適切な権限を付与します:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/git
完了したら、NginxWebサーバーの構成に進むことができます。
3Nginxを構成する
まず、GitトラフィックをGitに渡すようにNginxを構成する必要があります。これを行うには、Nginxのデフォルトの構成ファイルを編集します。
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
以下に示すようにファイルを変更します:
# Default server configuration
#
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
root /var/www/html/git;
# Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location / {
# First attempt to serve request as file, then
# as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404.
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ (/.*) {
client_max_body_size 0; # Git pushes can be massive, just to make sure nginx doesn't suddenly cut the connection add this.
auth_basic "Git Login"; # Whatever text will do.
auth_basic_user_file "/var/www/html/git/htpasswd";
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params; # Include the default fastcgi configs
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/lib/git-core/git-http-backend; # Tells fastcgi to pass the request to the git http backend executable
fastcgi_param GIT_HTTP_EXPORT_ALL "";
fastcgi_param GIT_PROJECT_ROOT /var/www/html/git; # /var/www/git is the location of all of your git repositories.
fastcgi_param REMOTE_USER $remote_user;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $1; # Takes the capture group from our location directive and gives git that.
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/fcgiwrap.socket; # Pass the request to fastcgi
}
} 終了したら、ファイルを保存して閉じます。次に、次のコマンドを使用して、構成エラーがないかNginxをテストします。
sudo nginx -t
すべてが正常であれば、次の出力が表示されます。
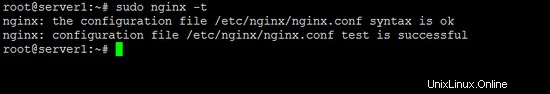
次に、リポジトリへのコミットを参照するために使用する必要があるユーザーアカウントを作成する必要があります。 htpasswdユーティリティを使用して、hiteshという名前のユーザーを作成できます。
sudo htpasswd -c /var/www/html/git/htpasswd hitesh
最後に、Nginxを再起動して、次のコマンドですべての変更を適用します。
sudo systemctl restart nginx
次のコマンドを使用して、Nginxサーバーのステータスを確認できます。
sudo systemctl status nginx
次の出力が表示されます。
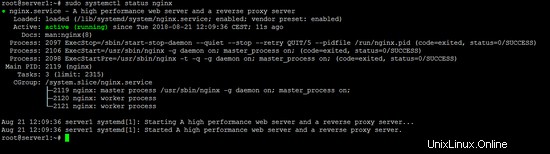
4Gitリポジトリを作成する
すべてが適切に構成されたら、Gitリポジトリを作成します。
次のコマンドを使用して、hitesh.gitという名前のリポジトリを作成できます。
cd /var/www/html/git
sudo mkdir hitesh.git
sudo cd hitesh.git
sudo git --bare init
sudo git update-server-info
sudo chown -R www-data.www-data .
sudo chmod -R 755 .
次に、UFWファイアウォールを介したHTTPサービスを許可する必要があります。デフォルトでは、UFWはシステムで無効になっているため、最初に有効にする必要があります。次のコマンドで有効にできます:
sudo ufw enable
UFWファイアウォールを有効にしたら、次のコマンドを実行してHTTPおよびSSHサービスを許可できます。
sudo ufw allow http
sudo ufw allow ssh
GITにはSSHは必要ありませんが、SSHを介してサーバーを管理できるようにする必要があります。
次のコマンドを実行して、UFWファイアウォールのステータスを確認できるようになりました。
sudo ufw status
サーバー側の構成は以上です。これで、クライアント側に移動してGitをテストできます。
5クライアントマシンでGitをテストする
開始する前に、クライアントシステムにgitをインストールする必要があります。次のコマンドでインストールできます:
sudo apt-get install git -y
まず、次のコマンドを使用してローカルリポジトリを作成します。
sudo mkdir ~/testproject
次に、ディレクトリを「testproject」に変更し、次のコマンドを使用して新しいリモートリポジトリを開始します。
cd ~/testproject
git init
git remote add origin http://[email protected]/hitesh.git
次に、次のコマンドを使用していくつかのファイルとディレクトリを作成します。
mkdir test1 test2 test3
echo "This is my first repository" > test1/repo1
echo "This is my second repository" > test2/repo2
echo "This is my third repository" > test3/repo3
次に、次のコマンドを実行して、すべてのファイルとディレクトリをリポジトリに追加します。
git add .
git commit -a -m "Add files and directories"
次の出力が表示されます。
[master 002fac9] Add files and directories 3 files changed, 3 insertions(+) create mode 100644 repo1 create mode 100644 repo2 create mode 100644 repo3
次に、次のコマンドを使用して、すべてのファイルとディレクトリをGitサーバーにプッシュします。
git push origin master
次の出力が表示されます。
Password for 'http://[email protected]': Counting objects: 6, done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (5/5), 422 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done. Total 5 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) To http://[email protected]/hitesh.git 68f1270..002fac9 master -> master
これで、すべてのファイルとディレクトリがGitサーバーにコミットされました。
これで、Gitリポジトリの作成プロセスが完了しました。これで、将来リポジトリのクローンを簡単に作成できます。リモートシステムで次のコマンドを使用して、リポジトリのクローンを作成できます。
git clone [email protected]:/var/www/html/git/hitesh.git
次の出力が表示されます。
Cloning into 'hitesh'... [email protected]'s password: remote: Counting objects: 8, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. Receiving objects: 100% (8/8), 598 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done. remote: Total 8 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) Checking connectivity... done.
次に、次のコマンドを使用して、ディレクトリを複製されたリポジトリに変更します。
cd hitesh
tree
次の出力が表示されます。
.
|-- test1
| `-- repo1
|-- test2
| `-- repo2
`-- test3
`-- repo3
3 directories, 3 files
このチュートリアルは、VMWareおよびVirtualboxと互換性のあるovf/ova形式の仮想マシンイメージをすぐに使用できる状態で利用できます。仮想マシンイメージは、次のログイン詳細を使用します:
SSH/シェルログイン
ユーザー名:管理者
パスワード:howtoforge
このユーザーにはsudo権限があります。
GITログイン
ユーザー名:hitesh
パスワード:howtoforge
VMのIPは192.168.1.100で、ファイル/etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yamlで変更できます。仮想マシンを保護するために、上記のすべてのパスワードを変更してください。
Gitサーバーを使用して、ソースコードを簡単にプッシュ、プル、クローン作成、およびコミットできるようになったことを願っています。ご不明な点がございましたら、お気軽にコメントしてください。
- Ubuntu
- Git