監視コマンドは非常に優れたツールであり、多くの状況で役立ちます。 watch コマンドを使用して、任意のファイルまたはスクリプトを定期的に監視できます。デフォルトでは 2 秒ごとに実行され、中断されるまで実行されます。
# watch -h Usage: watch [-dhntv] [--differences[=cumulative]] [--help] [--interval=[n]] [--no-title] [--version] [command] -d, --differences[=cumulative] highlight changes between updates (cumulative means highlighting is cumulative) -h, --help print a summary of the options -n, --interval=[seconds] seconds to wait between updates -v, --version print the version number -t, --no-title turns off showing the header
watch コマンドの基本的な構文は次のとおりです:
# watch [-n seconds] [-d] [command]
ここで、
-d flag will highlight the differences between successive updates. -n flag is to specify the interval. The default value is 2 seconds.
出力例は次のとおりです:
# watch -n 10 -d ls -lt Every 10.0s: ls -lt Tue Feb 14 12:27:43 2017 total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 12:27 new_file_just_created -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 10:46 file1 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 10:46 file2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 10:46 file3
ここで、
Every 10.0s : is the time interval to run the watch command. i.e. 10 seconds. ls -lt : is the command to be executed every 10 seconds. Tue Feb 14 12:27:43 2017 : is the current date and time.
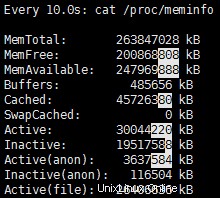
例 1 :/proc/meminfo のような動的に変化するファイルの監視
コマンド watch を使用して、システム上の任意のファイルを監視する方法があります。
コマンド:
# watch -n 10 -d cat /proc/meminfo
画面に10秒ごとにmeminfoステータスの出力を生成し、変更があれば強調表示します。
例 2 :ディレクトリの内容の変更を探す
watch コマンドのもう 1 つの優れた使用法は、ディレクトリの内容を監視し、新しいファイルが追加または削除されているかどうかを確認することです。
# watch -d ls -lt
ls コマンドの -lt スイッチは、最後に変更されたファイルを一番上に表示します。
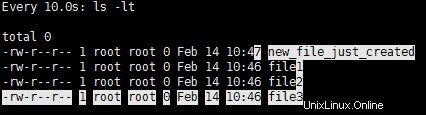
例 3 :出力からタイトル/ヘッダーを削除します。
watch コマンドの出力にヘッダーを出力したくない場合は、-no-title または -t オプションを使用できます。
# watch -t -d ls -lt total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 10:47 new_file_just_created -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 10:46 file1 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 10:46 file2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Feb 14 10:46 file3
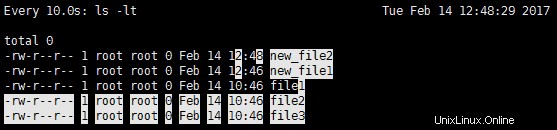
例 4 :累積差の強調表示
出力で累積差を強調したい場合は、コマンドで -d=cumulative スイッチを使用できます。例:
新しいファイルを追加した後の出力 – new_file1 :
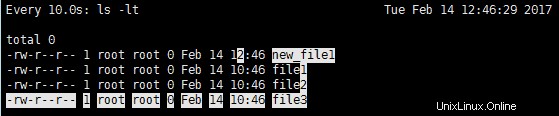
別の新しいファイルを追加した後の出力 – new_file2 :