PHP 設定にカスタム変更を加えようとしている場合でも、PHP バージョンを切り替えただけで間違った設定が読み込まれている場合でも、現在の PHP バージョンのデフォルトの PHP.ini ファイルが必要になる場合があります。以下では、このファイルが重要な理由について説明します。
PHP.ini ファイルは何をしますか?
php.ini ファイルには、実行時間、メモリ制限など、現在のすべての PHP 構成設定が含まれています。これは、memcache、APC などの PECL モジュールを有効にする方法でもあります。このファイルを使用すると、サーバーのデフォルトを上書きできます。構成設定。
新しい php.ini ファイルの設定
PHP.INI ファイルのコピーをロードする簡単な方法
PHP 構成オプションは、共有サーバー アカウント (リセラー アカウントを含む) で使用できます。専用/VPS アカウントには、PHP 構成オプションがロードされている場合のみ、PHP 構成オプションがあります。このオプションを使用すると、PHP.INI ファイルを手動で作成しなくてもすばやく簡単にロードできます。
<オール>これにより、デフォルトの PHP.INI ファイルが PUBLIC_HTML フォルダーに作成されます。
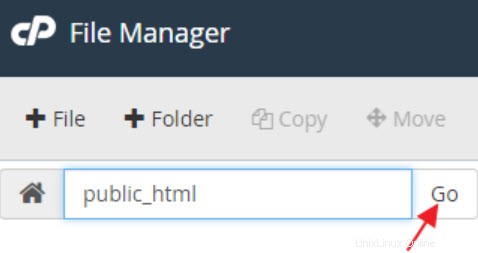
PHP.INI ファイルを手動で作成する方法
PHP バージョンのボタンをクリックすると、そのバージョンの正しい php.ini ファイルを含む新しいウィンドウが開きます。以下は、php.ini ファイルをアカウントに追加する手順です。
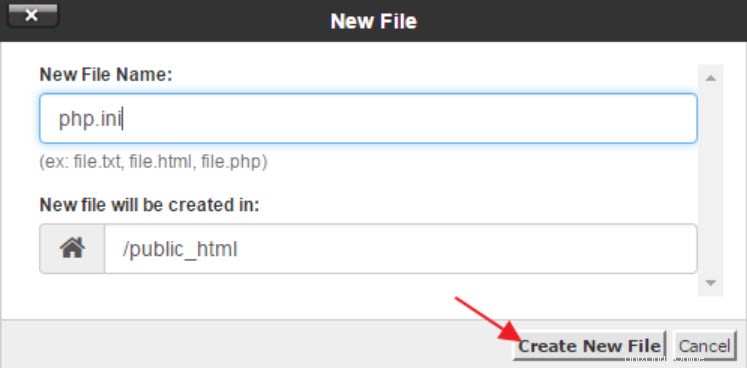
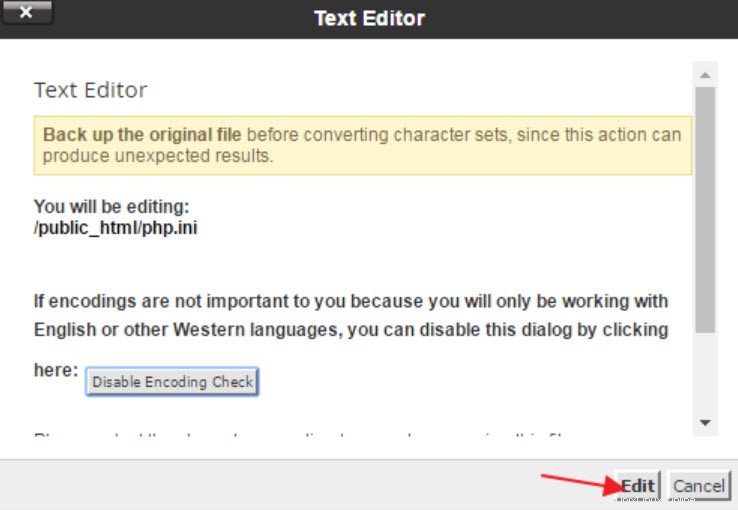
<オール>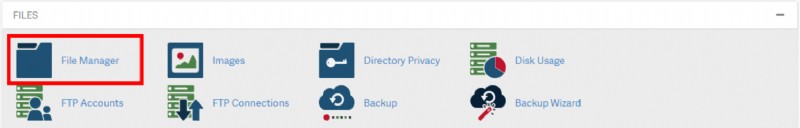
デフォルトの PHP 7 INI ファイル
[PHP]
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; About php.ini ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; PHP's initialization file, generally called php.ini, is responsible for
; configuring many of the aspects of PHP's behavior.
; PHP attempts to find and load this configuration from a number of locations.
; The following is a summary of its search order:
; 1. SAPI module specific location.
; 2. The PHPRC environment variable. (As of PHP 5.2.0)
; 3. A number of predefined registry keys on Windows (As of PHP 5.2.0)
; 4. Current working directory (except CLI)
; 5. The web server's directory (for SAPI modules), or directory of PHP
; (otherwise in Windows)
; 6. The directory from the --with-config-file-path compile time option, or the
; Windows directory (C:windows or C:winnt)
; See the PHP docs for more specific information.
; https://php.net/configuration.file
; The syntax of the file is extremely simple. Whitespace and lines
; beginning with a semicolon are silently ignored (as you probably guessed).
; Section headers (e.g. [Foo]) are also silently ignored, even though
; they might mean something in the future.
; Directives following the section heading [PATH=/www/mysite] only
; apply to PHP files in the /www/mysite directory. Directives
; following the section heading [HOST=www.example.com] only apply to
; PHP files served from www.example.com. Directives set in these
; special sections cannot be overridden by user-defined INI files or
; at runtime. Currently, [PATH=] and [HOST=] sections only work under
; CGI/FastCGI.
; https://php.net/ini.sections
; Directives are specified using the following syntax:
; directive = value
; Directive names are case sensitive - foo=bar is different from FOO=bar.
; Directives are variables used to configure PHP or PHP extensions.
; There is no name validation. If PHP can't find an expected
; directive because it is not set or is mistyped, a default value will be used.
; The value can be a string, a number, a PHP constant (e.g. E_ALL or M_PI), one
; of the INI constants (On, Off, True, False, Yes, No and None) or an expression
; (e.g. E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE), a quoted string ("bar"), or a reference to a
; previously set variable or directive (e.g. ${foo})
; Expressions in the INI file are limited to bitwise operators and parentheses:
; | bitwise OR
; ^ bitwise XOR
; & bitwise AND
; ~ bitwise NOT
; ! boolean NOT
; Boolean flags can be turned on using the values 1, On, True or Yes.
; They can be turned off using the values 0, Off, False or No.
; An empty string can be denoted by simply not writing anything after the equal
; sign, or by using the None keyword:
; foo = ; sets foo to an empty string
; foo = None ; sets foo to an empty string
; foo = "None" ; sets foo to the string 'None'
; If you use constants in your value, and these constants belong to a
; dynamically loaded extension (either a PHP extension or a Zend extension),
; you may only use these constants after the line that loads the extension.
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; About this file ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; PHP comes packaged with two INI files. One that is recommended to be used
; in production environments and one that is recommended to be used in
; development environments.
; php.ini-production contains settings which hold security, performance and
; best practices at its core. But please be aware, these settings may break
; compatibility with older or less security conscience applications. We
; recommending using the production ini in production and testing environments.
; php.ini-development is very similar to its production variant, except it is
; much more verbose when it comes to errors. We recommend using the
; development version only in development environments, as errors shown to
; application users can inadvertently leak otherwise secure information.
; This is php.ini-production INI file.
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Quick Reference ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; The following are all the settings which are different in either the production
; or development versions of the INIs with respect to PHP's default behavior.
; Please see the actual settings later in the document for more details as to why
; we recommend these changes in PHP's behavior.
; display_errors
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: Off
; display_startup_errors
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: Off
; error_reporting
; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED
; Development Value: E_ALL
; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
; html_errors
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: On
; Production value: On
; log_errors
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: On
; max_input_time
; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited)
; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds)
; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds)
; output_buffering
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: 4096
; Production Value: 4096
; register_argc_argv
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: Off
; Production Value: Off
; request_order
; Default Value: None
; Development Value: "GP"
; Production Value: "GP"
; session.gc_divisor
; Default Value: 100
; Development Value: 1000
; Production Value: 1000
; session.hash_bits_per_character
; Default Value: 4
; Development Value: 5
; Production Value: 5
; short_open_tag
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: Off
; Production Value: Off
; track_errors
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: Off
; url_rewriter.tags
; Default Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,form=,fieldset="
; Development Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
; Production Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
; variables_order
; Default Value: "EGPCS"
; Development Value: "GPCS"
; Production Value: "GPCS"
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; php.ini Options ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Name for user-defined php.ini (.htaccess) files. Default is ".user.ini"
;user_ini.filename = ".user.ini"
; To disable this feature set this option to empty value
;user_ini.filename =
; TTL for user-defined php.ini files (time-to-live) in seconds. Default is 300 seconds (5 minutes)
;user_ini.cache_ttl = 300
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Language Options ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Enable the PHP scripting language engine under Apache.
; https://php.net/engine
engine = On
; This directive determines whether or not PHP will recognize code between
; tags as PHP source which should be processed as such. It is
; generally recommended that should be used and that this feature
; should be disabled, as enabling it may result in issues when generating XML
; documents, however this remains supported for backward compatibility reasons.
; Note that this directive does not control the <?= shorthand tag, which can be
; used regardless of this directive.
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: Off
; Production Value: Off
; https://php.net/short-open-tag
short_open_tag = Off
; The number of significant digits displayed in floating point numbers.
; https://php.net/precision
precision = 14
; Output buffering is a mechanism for controlling how much output data
; (excluding headers and cookies) PHP should keep internally before pushing that
; data to the client. If your application's output exceeds this setting, PHP
; will send that data in chunks of roughly the size you specify.
; Turning on this setting and managing its maximum buffer size can yield some
; interesting side-effects depending on your application and web server.
; You may be able to send headers and cookies after you've already sent output
; through print or echo. You also may see performance benefits if your server is
; emitting less packets due to buffered output versus PHP streaming the output
; as it gets it. On production servers, 4096 bytes is a good setting for performance
; reasons.
; Note: Output buffering can also be controlled via Output Buffering Control
; functions.
; Possible Values:
; On = Enabled and buffer is unlimited. (Use with caution)
; Off = Disabled
; Integer = Enables the buffer and sets its maximum size in bytes.
; Note: This directive is hardcoded to Off for the CLI SAPI
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: 4096
; Production Value: 4096
; https://php.net/output-buffering
output_buffering = 4096
; You can redirect all of the output of your scripts to a function. For
; example, if you set output_handler to "mb_output_handler", character
; encoding will be transparently converted to the specified encoding.
; Setting any output handler automatically turns on output buffering.
; Note: People who wrote portable scripts should not depend on this ini
; directive. Instead, explicitly set the output handler using ob_start().
; Using this ini directive may cause problems unless you know what script
; is doing.
; Note: You cannot use both "mb_output_handler" with "ob_iconv_handler"
; and you cannot use both "ob_gzhandler" and "zlib.output_compression".
; Note: output_handler must be empty if this is set 'On' !!!!
; Instead you must use zlib.output_handler.
; https://php.net/output-handler
;output_handler =
; Transparent output compression using the zlib library
; Valid values for this option are 'off', 'on', or a specific buffer size
; to be used for compression (default is 4KB)
; Note: Resulting chunk size may vary due to nature of compression. PHP
; outputs chunks that are few hundreds bytes each as a result of
; compression. If you prefer a larger chunk size for better
; performance, enable output_buffering in addition.
; Note: You need to use zlib.output_handler instead of the standard
; output_handler, or otherwise the output will be corrupted.
; https://php.net/zlib.output-compression
zlib.output_compression = Off
; https://php.net/zlib.output-compression-level
;zlib.output_compression_level = -1
; You cannot specify additional output handlers if zlib.output_compression
; is activated here. This setting does the same as output_handler but in
; a different order.
; https://php.net/zlib.output-handler
;zlib.output_handler =
; Implicit flush tells PHP to tell the output layer to flush itself
; automatically after every output block. This is equivalent to calling the
; PHP function flush() after each and every call to print() or echo() and each
; and every HTML block. Turning this option on has serious performance
; implications and is generally recommended for debugging purposes only.
; https://php.net/implicit-flush
; Note: This directive is hardcoded to On for the CLI SAPI
implicit_flush = Off
; The unserialize callback function will be called (with the undefined class'
; name as parameter), if the unserializer finds an undefined class
; which should be instantiated. A warning appears if the specified function is
; not defined, or if the function doesn't include/implement the missing class.
; So only set this entry, if you really want to implement such a
; callback-function.
unserialize_callback_func =
; When floats & doubles are serialized store serialize_precision significant
; digits after the floating point. The default value ensures that when floats
; are decoded with unserialize, the data will remain the same.
serialize_precision = 17
; open_basedir, if set, limits all file operations to the defined directory
; and below. This directive makes most sense if used in a per-directory
; or per-virtualhost web server configuration file.
; https://php.net/open-basedir
;open_basedir =
; This directive allows you to disable certain functions for security reasons.
; It receives a comma-delimited list of function names.
; https://php.net/disable-functions
disable_functions =
; This directive allows you to disable certain classes for security reasons.
; It receives a comma-delimited list of class names.
; https://php.net/disable-classes
disable_classes =
; Colors for Syntax Highlighting mode. Anything that's acceptable in
; would work.
; https://php.net/syntax-highlighting
;highlight.string = #DD0000
;highlight.comment = #FF9900
;highlight.keyword = #007700
;highlight.default = #0000BB
;highlight.html = #000000
; If enabled, the request will be allowed to complete even if the user aborts
; the request. Consider enabling it if executing long requests, which may end up
; being interrupted by the user or a browser timing out. PHP's default behavior
; is to disable this feature.
; https://php.net/ignore-user-abort
;ignore_user_abort = On
; Determines the size of the realpath cache to be used by PHP. This value should
; be increased on systems where PHP opens many files to reflect the quantity of
; the file operations performed.
; https://php.net/realpath-cache-size
;realpath_cache_size = 16k
; Duration of time, in seconds for which to cache realpath information for a given
; file or directory. For systems with rarely changing files, consider increasing this
; value.
; https://php.net/realpath-cache-ttl
;realpath_cache_ttl = 120
; Enables or disables the circular reference collector.
; https://php.net/zend.enable-gc
zend.enable_gc = On
; If enabled, scripts may be written in encodings that are incompatible with
; the scanner. CP936, Big5, CP949 and Shift_JIS are the examples of such
; encodings. To use this feature, mbstring extension must be enabled.
; Default: Off
;zend.multibyte = Off
; Allows to set the default encoding for the scripts. This value will be used
; unless "declare(encoding=…)" directive appears at the top of the script.
; Only affects if zend.multibyte is set.
; Default: ""
;zend.script_encoding =
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Miscellaneous ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Decides whether PHP may expose the fact that it is installed on the server
; (e.g. by adding its signature to the Web server header). It is no security
; threat in any way, but it makes it possible to determine whether you use PHP
; on your server or not.
; https://php.net/expose-php
expose_php = On
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Resource Limits ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Maximum execution time of each script, in seconds
; https://php.net/max-execution-time
; Note: This directive is hardcoded to 0 for the CLI SAPI
max_execution_time = 30
; Maximum amount of time each script may spend parsing request data. It's a good
; idea to limit this time on productions servers in order to eliminate unexpectedly
; long running scripts.
; Note: This directive is hardcoded to -1 for the CLI SAPI
; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited)
; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds)
; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds)
; https://php.net/max-input-time
max_input_time = 60
; Maximum input variable nesting level
; https://php.net/max-input-nesting-level
;max_input_nesting_level = 64
; How many GET/POST/COOKIE input variables may be accepted
; max_input_vars = 1000
; Maximum amount of memory a script may consume (128MB)
; https://php.net/memory-limit
memory_limit = 128M
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Error handling and logging ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; This directive informs PHP of which errors, warnings and notices you would like
; it to take action for. The recommended way of setting values for this
; directive is through the use of the error level constants and bitwise
; operators. The error level constants are below here for convenience as well as
; some common settings and their meanings.
; By default, PHP is set to take action on all errors, notices and warnings EXCEPT
; those related to E_NOTICE and E_STRICT, which together cover best practices and
; recommended coding standards in PHP. For performance reasons, this is the
; recommend error reporting setting. Your production server shouldn't be wasting
; resources complaining about best practices and coding standards. That's what
; development servers and development settings are for.
; Note: The php.ini-development file has this setting as E_ALL. This
; means it pretty much reports everything which is exactly what you want during
; development and early testing.
;
; Error Level Constants:
; E_ALL - All errors and warnings (includes E_STRICT as of PHP 5.4.0)
; E_ERROR - fatal run-time errors
; E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR - almost fatal run-time errors
; E_WARNING - run-time warnings (non-fatal errors)
; E_PARSE - compile-time parse errors
; E_NOTICE - run-time notices (these are warnings which often result
; from a bug in your code, but it's possible that it was
; intentional (e.g., using an uninitialized variable and
; relying on the fact it is automatically initialized to an
; empty string)
; E_STRICT - run-time notices, enable to have PHP suggest changes
; to your code which will ensure the best interoperability
; and forward compatibility of your code
; E_CORE_ERROR - fatal errors that occur during PHP's initial startup
; E_CORE_WARNING - warnings (non-fatal errors) that occur during PHP's
; initial startup
; E_COMPILE_ERROR - fatal compile-time errors
; E_COMPILE_WARNING - compile-time warnings (non-fatal errors)
; E_USER_ERROR - user-generated error message
; E_USER_WARNING - user-generated warning message
; E_USER_NOTICE - user-generated notice message
; E_DEPRECATED - warn about code that will not work in future versions
; of PHP
; E_USER_DEPRECATED - user-generated deprecation warnings
;
; Common Values:
; E_ALL (Show all errors, warnings and notices including coding standards.)
; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE (Show all errors, except for notices)
; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT (Show all errors, except for notices and coding standards warnings.)
; E_COMPILE_ERROR|E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR|E_ERROR|E_CORE_ERROR (Show only errors)
; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED
; Development Value: E_ALL
; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
; https://php.net/error-reporting
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
; This directive controls whether or not and where PHP will output errors,
; notices and warnings too. Error output is very useful during development, but
; it could be very dangerous in production environments. Depending on the code
; which is triggering the error, sensitive information could potentially leak
; out of your application such as database usernames and passwords or worse.
; For production environments, we recommend logging errors rather than
; sending them to STDOUT.
; Possible Values:
; Off = Do not display any errors
; stderr = Display errors to STDERR (affects only CGI/CLI binaries!)
; On or stdout = Display errors to STDOUT
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: Off
; https://php.net/display-errors
display_errors = Off
; The display of errors which occur during PHP's startup sequence are handled
; separately from display_errors. PHP's default behavior is to suppress those
; errors from clients. Turning the display of startup errors on can be useful in
; debugging configuration problems. We strongly recommend you
; set this to 'off' for production servers.
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: Off
; https://php.net/display-startup-errors
display_startup_errors = Off
; Besides displaying errors, PHP can also log errors to locations such as a
; server-specific log, STDERR, or a location specified by the error_log
; directive found below. While errors should not be displayed on productions
; servers they should still be monitored and logging is a great way to do that.
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: On
; https://php.net/log-errors
log_errors = On
; Set maximum length of log_errors. In error_log information about the source is
; added. The default is 1024 and 0 allows to not apply any maximum length at all.
; https://php.net/log-errors-max-len
log_errors_max_len = 1024
; Do not log repeated messages. Repeated errors must occur in same file on same
; line unless ignore_repeated_source is set true.
; https://php.net/ignore-repeated-errors
ignore_repeated_errors = Off
; Ignore source of message when ignoring repeated messages. When this setting
; is On you will not log errors with repeated messages from different files or
; source lines.
; https://php.net/ignore-repeated-source
ignore_repeated_source = Off
; If this parameter is set to Off, then memory leaks will not be shown (on
; stdout or in the log). This has only effect in a debug compile, and if
; error reporting includes E_WARNING in the allowed list
; https://php.net/report-memleaks
report_memleaks = On
; This setting is on by default.
;report_zend_debug = 0
; Store the last error/warning message in $php_errormsg (boolean). Setting this value
; to On can assist in debugging and is appropriate for development servers. It should
; however be disabled on production servers.
; Default Value: Off
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: Off
; https://php.net/track-errors
track_errors = Off
; Turn off normal error reporting and emit XML-RPC error XML
; https://php.net/xmlrpc-errors
;xmlrpc_errors = 0
; An XML-RPC faultCode
;xmlrpc_error_number = 0
; When PHP displays or logs an error, it has the capability of formatting the
; error message as HTML for easier reading. This directive controls whether
; the error message is formatted as HTML or not.
; Note: This directive is hardcoded to Off for the CLI SAPI
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: On
; Production value: On
; https://php.net/html-errors
html_errors = On
; If html_errors is set to On and docref_root is not empty, then PHP
; produces clickable error messages that direct to a page describing the error
; or function causing the error in detail.
; You can download a copy of the PHP manual from https://php.net/docs
; and change docref_root to the base URL of your local copy including the
; leading '/'. You must also specify the file extension being used including
; the dot. PHP's default behavior is to leave these settings empty, in which
; case no links to documentation are generated.
; Note: Never use this feature for production boxes.
; https://php.net/docref-root
; Examples
;docref_root = "/phpmanual/"
; https://php.net/docref-ext
;docref_ext = .html
; String to output before an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave
; this setting blank.
; https://php.net/error-prepend-string
; Example:
;error_prepend_string = ""
; String to output after an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave
; this setting blank.
; https://php.net/error-append-string
; Example:
;error_append_string = ""
; Log errors to specified file. PHP's default behavior is to leave this value
; empty.
; https://php.net/error-log
; Example:
;error_log = php_errors.log
; Log errors to syslog (Event Log on Windows).
;error_log = syslog
;windows.show_crt_warning
; Default value: 0
; Development value: 0
; Production value: 0
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Data Handling ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; The separator used in PHP generated URLs to separate arguments.
; PHP's default setting is "&".
; https://php.net/arg-separator.output
; Example:
;arg_separator.output = "&"
; List of separator(s) used by PHP to parse input URLs into variables.
; PHP's default setting is "&".
; NOTE: Every character in this directive is considered as separator!
; https://php.net/arg-separator.input
; Example:
;arg_separator.input = ";&"
; This directive determines which super global arrays are registered when PHP
; starts up. G,P,C,E & S are abbreviations for the following respective super
; globals: GET, POST, COOKIE, ENV and SERVER. There is a performance penalty
; paid for the registration of these arrays and because ENV is not as commonly
; used as the others, ENV is not recommended on productions servers. You
; can still get access to the environment variables through getenv() should you
; need to.
; Default Value: "EGPCS"
; Development Value: "GPCS"
; Production Value: "GPCS";
; https://php.net/variables-order
variables_order = "GPCS"
; This directive determines which super global data (G,P & C) should be
; registered into the super global array REQUEST. If so, it also determines
; the order in which that data is registered. The values for this directive
; are specified in the same manner as the variables_order directive,
; EXCEPT one. Leaving this value empty will cause PHP to use the value set
; in the variables_order directive. It does not mean it will leave the super
; globals array REQUEST empty.
; Default Value: None
; Development Value: "GP"
; Production Value: "GP"
; https://php.net/request-order
request_order = "GP"
; This directive determines whether PHP registers $argv & $argc each time it
; runs. $argv contains an array of all the arguments passed to PHP when a script
; is invoked. $argc contains an integer representing the number of arguments
; that were passed when the script was invoked. These arrays are extremely
; useful when running scripts from the command line. When this directive is
; enabled, registering these variables consumes CPU cycles and memory each time
; a script is executed. For performance reasons, this feature should be disabled
; on production servers.
; Note: This directive is hardcoded to On for the CLI SAPI
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: Off
; Production Value: Off
; https://php.net/register-argc-argv
register_argc_argv = Off
; When enabled, the ENV, REQUEST and SERVER variables are created when they're
; first used (Just In Time) instead of when the script starts. If these
; variables are not used within a script, having this directive on will result
; in a performance gain. The PHP directive register_argc_argv must be disabled
; for this directive to have any affect.
; https://php.net/auto-globals-jit
auto_globals_jit = On
; Whether PHP will read the POST data.
; This option is enabled by default.
; Most likely, you won't want to disable this option globally. It causes $_POST
; and $_FILES to always be empty; the only way you will be able to read the
; POST data will be through the php://input stream wrapper. This can be useful
; to proxy requests or to process the POST data in a memory efficient fashion.
; https://php.net/enable-post-data-reading
;enable_post_data_reading = Off
; Maximum size of POST data that PHP will accept.
; Its value may be 0 to disable the limit. It is ignored if POST data reading
; is disabled through enable_post_data_reading.
; https://php.net/post-max-size
post_max_size = 8M
; Automatically add files before PHP document.
; https://php.net/auto-prepend-file
auto_prepend_file =
; Automatically add files after PHP document.
; https://php.net/auto-append-file
auto_append_file =
; By default, PHP will output a media type using the Content-Type header. To
; disable this, simply set it to be empty.
;
; PHP's built-in default media type is set to text/html.
; https://php.net/default-mimetype
default_mimetype = "text/html"
; PHP's default character set is set to UTF-8.
; https://php.net/default-charset
default_charset = "UTF-8"
; PHP internal character encoding is set to empty.
; If empty, default_charset is used.
; https://php.net/internal-encoding
;internal_encoding =
; PHP input character encoding is set to empty.
; If empty, default_charset is used.
; https://php.net/input-encoding
;input_encoding =
; PHP output character encoding is set to empty.
; If empty, default_charset is used.
; mbstring or iconv output handler is used.
; See also output_buffer.
; https://php.net/output-encoding
;output_encoding =
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Paths and Directories ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; UNIX: "/path1:/path2"
;include_path = ".:/php/includes"
;
; Windows: "path1;path2"
;include_path = ".;c:phpincludes"
;
; PHP's default setting for include_path is ".;/path/to/php/pear"
; https://php.net/include-path
; The root of the PHP pages, used only if nonempty.
; if PHP was not compiled with FORCE_REDIRECT, you SHOULD set doc_root
; if you are running php as a CGI under any web server (other than IIS)
; see documentation for security issues. The alternate is to use the
; cgi.force_redirect configuration below
; https://php.net/doc-root
doc_root =
; The directory under which PHP opens the script using /~username used only
; if nonempty.
; https://php.net/user-dir
user_dir =
; Directory in which the loadable extensions (modules) reside.
; https://php.net/extension-dir
; extension_dir = "./"
; On windows:
; extension_dir = "ext"
; Directory where the temporary files should be placed.
; Defaults to the system default (see sys_get_temp_dir)
; sys_temp_dir = "/tmp"
; Whether or not to enable the dl() function. The dl() function does NOT work
; properly in multithreaded servers, such as IIS or Zeus, and is automatically
; disabled on them.
; https://php.net/enable-dl
enable_dl = Off
; cgi.force_redirect is necessary to provide security running PHP as a CGI under
; most web servers. Left undefined, PHP turns this on by default. You can
; turn it off here AT YOUR OWN RISK
; You CAN safely turn this off for IIS, in fact, you MUST.
; https://php.net/cgi.force-redirect
;cgi.force_redirect = 1
; if cgi.nph is enabled it will force cgi to always sent Status: 200 with
; every request. PHP's default behavior is to disable this feature.
;cgi.nph = 1
; if cgi.force_redirect is turned on, and you are not running under Apache or Netscape
; (iPlanet) web servers, you MAY need to set an environment variable name that PHP
; will look for to know it is OK to continue execution. Setting this variable MAY
; cause security issues, KNOW WHAT YOU ARE DOING FIRST.
; https://php.net/cgi.redirect-status-env
;cgi.redirect_status_env =
; cgi.fix_pathinfo provides real PATH_INFO/PATH_TRANSLATED support for CGI. PHP's
; previous behaviour was to set PATH_TRANSLATED to SCRIPT_FILENAME, and to not grok
; what PATH_INFO is. For more information on PATH_INFO, see the cgi specs. Setting
; this to 1 will cause PHP CGI to fix its paths to conform to the spec. A setting
; of zero causes PHP to behave as before. Default is 1. You should fix your scripts
; to use SCRIPT_FILENAME rather than PATH_TRANSLATED.
; https://php.net/cgi.fix-pathinfo
;cgi.fix_pathinfo=1
; FastCGI under IIS (on WINNT based OS) supports the ability to impersonate
; security tokens of the calling client. This allows IIS to define the
; security context that the request runs under. mod_fastcgi under Apache
; does not currently support this feature (03/17/2002)
; Set to 1 if running under IIS. Default is zero.
; https://php.net/fastcgi.impersonate
;fastcgi.impersonate = 1
; Disable logging through FastCGI connection. PHP's default behavior is to enable
; this feature.
;fastcgi.logging = 0
; cgi.rfc2616_headers configuration option tells PHP what type of headers to
; use when sending HTTP response code. If set to 0, PHP sends Status: header that
; is supported by Apache. When this option is set to 1, PHP will send
; RFC2616 compliant header.
; Default is zero.
; https://php.net/cgi.rfc2616-headers
;cgi.rfc2616_headers = 0
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; File Uploads ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Whether to allow HTTP file uploads.
; https://php.net/file-uploads
file_uploads = On
; Temporary directory for HTTP uploaded files (will use system default if not
; specified).
; https://php.net/upload-tmp-dir
;upload_tmp_dir =
; Maximum allowed size for uploaded files.
; https://php.net/upload-max-filesize
upload_max_filesize = 2M
; Maximum number of files that can be uploaded via a single request
max_file_uploads = 20
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Fopen wrappers ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Whether to allow the treatment of URLs (like https:// or ftp://) as files.
; https://php.net/allow-url-fopen
allow_url_fopen = On
; Whether to allow include/require to open URLs (like https:// or ftp://) as files.
; https://php.net/allow-url-include
allow_url_include = Off
; Define the anonymous ftp password (your email address). PHP's default setting
; for this is empty.
; https://php.net/from
;from="example@unixlinux.online"
; Define the User-Agent string. PHP's default setting for this is empty.
; https://php.net/user-agent
;user_agent="PHP"
; Default timeout for socket based streams (seconds)
; https://php.net/default-socket-timeout
default_socket_timeout = 60
; If your scripts have to deal with files from Macintosh systems,
; or you are running on a Mac and need to deal with files from
; unix or win32 systems, setting this flag will cause PHP to
; automatically detect the EOL character in those files so that
; fgets() and file() will work regardless of the source of the file.
; https://php.net/auto-detect-line-endings
;auto_detect_line_endings = Off
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Dynamic Extensions ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; If you wish to have an extension loaded automatically, use the following
; syntax:
;
; extension=modulename.extension
;
; For example, on Windows:
;
; extension=msql.dll
;
; … or under UNIX:
;
; extension=msql.so
;
; … or with a path:
;
; extension=/path/to/extension/msql.so
;
; If you only provide the name of the extension, PHP will look for it in its
; default extension directory.
;
; Windows Extensions
; Note that ODBC support is built in, so no dll is needed for it.
; Note that many DLL files are located in the extensions/ (PHP 4) ext/ (PHP 5+)
; extension folders as well as the separate PECL DLL download (PHP 5+).
; Be sure to appropriately set the extension_dir directive.
;
;extension=php_bz2.dll
;extension=php_curl.dll
;extension=php_fileinfo.dll
;extension=php_gd2.dll
;extension=php_gettext.dll
;extension=php_gmp.dll
;extension=php_intl.dll
;extension=php_imap.dll
;extension=php_interbase.dll
;extension=php_ldap.dll
;extension=php_mbstring.dll
;extension=php_exif.dll ; Must be after mbstring as it depends on it
;extension=php_mysqli.dll
;extension=php_oci8_12c.dll ; Use with Oracle Database 12c Instant Client
;extension=php_openssl.dll
;extension=php_pdo_firebird.dll
;extension=php_pdo_mysql.dll
;extension=php_pdo_oci.dll
;extension=php_pdo_odbc.dll
;extension=php_pdo_pgsql.dll
;extension=php_pdo_sqlite.dll
;extension=php_pgsql.dll
;extension=php_shmop.dll
; The MIBS data available in the PHP distribution must be installed.
; See https://www.php.net/manual/en/snmp.installation.php
;extension=php_snmp.dll
;extension=php_soap.dll
;extension=php_sockets.dll
;extension=php_sqlite3.dll
;extension=php_tidy.dll
;extension=php_xmlrpc.dll
;extension=php_xsl.dll
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Module Settings ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
[CLI Server]
; Whether the CLI web server uses ANSI color coding in its terminal output.
cli_server.color = On
[Date]
; Defines the default timezone used by the date functions
; https://php.net/date.timezone
;date.timezone =
; https://php.net/date.default-latitude
;date.default_latitude = 31.7667
; https://php.net/date.default-longitude
;date.default_longitude = 35.2333
; https://php.net/date.sunrise-zenith
;date.sunrise_zenith = 90.583333
; https://php.net/date.sunset-zenith
;date.sunset_zenith = 90.583333
[filter]
; https://php.net/filter.default
;filter.default = unsafe_raw
; https://php.net/filter.default-flags
;filter.default_flags =
[iconv]
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global input_encoding instead.
; If empty, default_charset or input_encoding or iconv.input_encoding is used.
; The precedence is: default_charset < intput_encoding < iconv.input_encoding
;iconv.input_encoding =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global internal_encoding instead.
; If empty, default_charset or internal_encoding or iconv.internal_encoding is used.
; The precedence is: default_charset < internal_encoding < iconv.internal_encoding
;iconv.internal_encoding =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global output_encoding instead.
; If empty, default_charset or output_encoding or iconv.output_encoding is used.
; The precedence is: default_charset < output_encoding < iconv.output_encoding
; To use an output encoding conversion, iconv's output handler must be set
; otherwise output encoding conversion cannot be performed.
;iconv.output_encoding =
[intl]
;intl.default_locale =
; This directive allows you to produce PHP errors when some error
; happens within intl functions. The value is the level of the error produced.
; Default is 0, which does not produce any errors.
;intl.error_level = E_WARNING
[sqlite3]
;sqlite3.extension_dir =
[Pcre]
;PCRE library backtracking limit.
; https://php.net/pcre.backtrack-limit
;pcre.backtrack_limit=100000
;PCRE library recursion limit.
;Please note that if you set this value to a high number you may consume all
;the available process stack and eventually crash PHP (due to reaching the
;stack size limit imposed by the Operating System).
; https://php.net/pcre.recursion-limit
;pcre.recursion_limit=100000
;Enables or disables JIT compilation of patterns. This requires the PCRE
;library to be compiled with JIT support.
;pcre.jit=1
[Pdo]
; Whether to pool ODBC connections. Can be one of "strict", "relaxed" or "off"
; https://php.net/pdo-odbc.connection-pooling
;pdo_odbc.connection_pooling=strict
;pdo_odbc.db2_instance_name
[Pdo_mysql]
; If mysqlnd is used: Number of cache slots for the internal result set cache
; https://php.net/pdo_mysql.cache_size
pdo_mysql.cache_size = 2000
; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in
; MySQL defaults.
; https://php.net/pdo_mysql.default-socket
pdo_mysql.default_socket=
[Phar]
; https://php.net/phar.readonly
;phar.readonly = On
; https://php.net/phar.require-hash
;phar.require_hash = On
;phar.cache_list =
[mail function]
; For Win32 only.
; https://php.net/smtp
SMTP = localhost
; https://php.net/smtp-port
smtp_port = 25
; For Win32 only.
; https://php.net/sendmail-from
;sendmail_from = example@unixlinux.online
; For Unix only. You may supply arguments as well (default: "sendmail -t -i").
; https://php.net/sendmail-path
;sendmail_path =
; Force the addition of the specified parameters to be passed as extra parameters
; to the sendmail binary. These parameters will always replace the value of
; the 5th parameter to mail().
;mail.force_extra_parameters =
; Add X-PHP-Originating-Script: that will include uid of the script followed by the filename
mail.add_x_header = On
; The path to a log file that will log all mail() calls. Log entries include
; the full path of the script, line number, To address and headers.
;mail.log =
; Log mail to syslog (Event Log on Windows).
;mail.log = syslog
[SQL]
; https://php.net/sql.safe-mode
sql.safe_mode = Off
[ODBC]
; https://php.net/odbc.default-db
;odbc.default_db = Not yet implemented
; https://php.net/odbc.default-user
;odbc.default_user = Not yet implemented
; https://php.net/odbc.default-pw
;odbc.default_pw = Not yet implemented
; Controls the ODBC cursor model.
; Default: SQL_CURSOR_STATIC (default).
;odbc.default_cursortype
; Allow or prevent persistent links.
; https://php.net/odbc.allow-persistent
odbc.allow_persistent = On
; Check that a connection is still valid before reuse.
; https://php.net/odbc.check-persistent
odbc.check_persistent = On
; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit.
; https://php.net/odbc.max-persistent
odbc.max_persistent = -1
; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit.
; https://php.net/odbc.max-links
odbc.max_links = -1
; Handling of LONG fields. Returns number of bytes to variables. 0 means
; passthru.
; https://php.net/odbc.defaultlrl
odbc.defaultlrl = 4096
; Handling of binary data. 0 means passthru, 1 return as is, 2 convert to char.
; See the documentation on odbc_binmode and odbc_longreadlen for an explanation
; of odbc.defaultlrl and odbc.defaultbinmode
; https://php.net/odbc.defaultbinmode
odbc.defaultbinmode = 1
;birdstep.max_links = -1
[Interbase]
; Allow or prevent persistent links.
ibase.allow_persistent = 1
; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit.
ibase.max_persistent = -1
; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit.
ibase.max_links = -1
; Default database name for ibase_connect().
;ibase.default_db =
; Default username for ibase_connect().
;ibase.default_user =
; Default password for ibase_connect().
;ibase.default_password =
; Default charset for ibase_connect().
;ibase.default_charset =
; Default timestamp format.
ibase.timestampformat = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
; Default date format.
ibase.dateformat = "%Y-%m-%d"
; Default time format.
ibase.timeformat = "%H:%M:%S"
[MySQLi]
; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit.
; https://php.net/mysqli.max-persistent
mysqli.max_persistent = -1
; Allow accessing, from PHP's perspective, local files with LOAD DATA statements
; https://php.net/mysqli.allow_local_infile
;mysqli.allow_local_infile = On
; Allow or prevent persistent links.
; https://php.net/mysqli.allow-persistent
mysqli.allow_persistent = On
; Maximum number of links. -1 means no limit.
; https://php.net/mysqli.max-links
mysqli.max_links = -1
; If mysqlnd is used: Number of cache slots for the internal result set cache
; https://php.net/mysqli.cache_size
mysqli.cache_size = 2000
; Default port number for mysqli_connect(). If unset, mysqli_connect() will use
; the $MYSQL_TCP_PORT or the mysql-tcp entry in /etc/services or the
; compile-time value defined MYSQL_PORT (in that order). Win32 will only look
; at MYSQL_PORT.
; https://php.net/mysqli.default-port
mysqli.default_port = 3306
; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in
; MySQL defaults.
; https://php.net/mysqli.default-socket
mysqli.default_socket =
; Default host for mysql_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode).
; https://php.net/mysqli.default-host
mysqli.default_host =
; Default user for mysql_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode).
; https://php.net/mysqli.default-user
mysqli.default_user =
; Default password for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode).
; Note that this is generally a bad idea to store passwords in this file.
; Any user with PHP access can run 'echo get_cfg_var("mysqli.default_pw")
; and reveal this password! And of course, any users with read access to this
; file will be able to reveal the password as well.
; https://php.net/mysqli.default-pw
mysqli.default_pw =
; Allow or prevent reconnect
mysqli.reconnect = Off
[mysqlnd]
; Enable / Disable collection of general statistics by mysqlnd which can be
; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations.
; https://php.net/mysqlnd.collect_statistics
mysqlnd.collect_statistics = On
; Enable / Disable collection of memory usage statistics by mysqlnd which can be
; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations.
; https://php.net/mysqlnd.collect_memory_statistics
mysqlnd.collect_memory_statistics = Off
; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used when sending commands to MySQL in bytes.
; https://php.net/mysqlnd.net_cmd_buffer_size
;mysqlnd.net_cmd_buffer_size = 2048
; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used for reading data sent by the server in
; bytes.
; https://php.net/mysqlnd.net_read_buffer_size
;mysqlnd.net_read_buffer_size = 32768
[OCI8]
; Connection: Enables privileged connections using external
; credentials (OCI_SYSOPER, OCI_SYSDBA)
; https://php.net/oci8.privileged-connect
;oci8.privileged_connect = Off
; Connection: The maximum number of persistent OCI8 connections per
; process. Using -1 means no limit.
; https://php.net/oci8.max-persistent
;oci8.max_persistent = -1
; Connection: The maximum number of seconds a process is allowed to
; maintain an idle persistent connection. Using -1 means idle
; persistent connections will be maintained forever.
; https://php.net/oci8.persistent-timeout
;oci8.persistent_timeout = -1
; Connection: The number of seconds that must pass before issuing a
; ping during oci_pconnect() to check the connection validity. When
; set to 0, each oci_pconnect() will cause a ping. Using -1 disables
; pings completely.
; https://php.net/oci8.ping-interval
;oci8.ping_interval = 60
; Connection: Set this to a user chosen connection class to be used
; for all pooled server requests with Oracle 11g Database Resident
; Connection Pooling (DRCP). To use DRCP, this value should be set to
; the same string for all web servers running the same application,
; the database pool must be configured, and the connection string must
; specify to use a pooled server.
;oci8.connection_class =
; High-Availability: Using On lets PHP receive Fast Application
; Notification (FAN) events generated when a database node fails. The
; database must also be configured to post FAN events.
;oci8.events = Off
; Tuning: This option enables statement caching, and specifies how
; many statements to cache. Using 0 disables statement caching.
; https://php.net/oci8.statement-cache-size
;oci8.statement_cache_size = 20
; Tuning: Enables statement prefetching and sets the default number of
; rows that will be fetched automatically after statement execution.
; https://php.net/oci8.default-prefetch
;oci8.default_prefetch = 100
; Compatibility. Using On means oci_close() will not close
; oci_connect() and oci_new_connect() connections.
; https://php.net/oci8.old-oci-close-semantics
;oci8.old_oci_close_semantics = Off
[PostgreSQL]
; Allow or prevent persistent links.
; https://php.net/pgsql.allow-persistent
pgsql.allow_persistent = On
; Detect broken persistent links always with pg_pconnect().
; Auto reset feature requires a little overheads.
; https://php.net/pgsql.auto-reset-persistent
pgsql.auto_reset_persistent = Off
; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit.
; https://php.net/pgsql.max-persistent
pgsql.max_persistent = -1
; Maximum number of links (persistent+non persistent). -1 means no limit.
; https://php.net/pgsql.max-links
pgsql.max_links = -1
; Ignore PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not.
; Notice message logging require a little overheads.
; https://php.net/pgsql.ignore-notice
pgsql.ignore_notice = 0
; Log PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not.
; Unless pgsql.ignore_notice=0, module cannot log notice message.
; https://php.net/pgsql.log-notice
pgsql.log_notice = 0
[bcmath]
; Number of decimal digits for all bcmath functions.
; https://php.net/bcmath.scale
bcmath.scale = 0
[browscap]
; https://php.net/browscap
;browscap = extra/browscap.ini
[Session]
; Handler used to store/retrieve data.
; https://php.net/session.save-handler
session.save_handler = files
; Argument passed to save_handler. In the case of files, this is the path
; where data files are stored. Note: Windows users have to change this
; variable in order to use PHP's session functions.
;
; The path can be defined as:
;
; session.save_path = "N;/path"
;
; where N is an integer. Instead of storing all the session files in
; /path, what this will do is use subdirectories N-levels deep, and
; store the session data in those directories. This is useful if
; your OS has problems with many files in one directory, and is
; a more efficient layout for servers that handle many sessions.
;
; NOTE 1: PHP will not create this directory structure automatically.
; You can use the script in the ext/session dir for that purpose.
; NOTE 2: See the section on garbage collection below if you choose to
; use subdirectories for session storage
;
; The file storage module creates files using mode 600 by default.
; You can change that by using
;
; session.save_path = "N;MODE;/path"
;
; where MODE is the octal representation of the mode. Note that this
; does not overwrite the process's umask.
; https://php.net/session.save-path
;session.save_path = "/tmp"
; Whether to use strict session mode.
; Strict session mode does not accept uninitialized session ID and regenerate
; session ID if browser sends uninitialized session ID. Strict mode protects
; applications from session fixation via session adoption vulnerability. It is
; disabled by default for maximum compatibility, but enabling it is encouraged.
; https://wiki.php.net/rfc/strict_sessions
session.use_strict_mode = 0
; Whether to use cookies.
; https://php.net/session.use-cookies
session.use_cookies = 1
; https://php.net/session.cookie-secure
;session.cookie_secure =
; This option forces PHP to fetch and use a cookie for storing and maintaining
; the session id. We encourage this operation as it's very helpful in combating
; session hijacking when not specifying and managing your own session id. It is
; not the be-all and end-all of session hijacking defense, but it's a good start.
; https://php.net/session.use-only-cookies
session.use_only_cookies = 1
; Name of the session (used as cookie name).
; https://php.net/session.name
session.name = PHPSESSID
; Initialize session on request startup.
; https://php.net/session.auto-start
session.auto_start = 0
; Lifetime in seconds of cookie or, if 0, until browser is restarted.
; https://php.net/session.cookie-lifetime
session.cookie_lifetime = 0
; The path for which the cookie is valid.
; https://php.net/session.cookie-path
session.cookie_path = /
; The domain for which the cookie is valid.
; https://php.net/session.cookie-domain
session.cookie_domain =
; Whether or not to add the httpOnly flag to the cookie, which makes it inaccessible to browser scripting languages such as JavaScript.
; https://php.net/session.cookie-httponly
session.cookie_httponly =
; Handler used to serialize data. php is the standard serializer of PHP.
; https://php.net/session.serialize-handler
session.serialize_handler = php
; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started
; on every session initialization. The probability is calculated by using
; gc_probability/gc_divisor. Where session.gc_probability is the numerator
; and gc_divisor is the denominator in the equation. Setting this value to 1
; when the session.gc_divisor value is 100 will give you approximately a 1% chance
; the gc will run on any give request.
; Default Value: 1
; Development Value: 1
; Production Value: 1
; https://php.net/session.gc-probability
session.gc_probability = 1
; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started on every
; session initialization. The probability is calculated by using the following equation:
; gc_probability/gc_divisor. Where session.gc_probability is the numerator and
; session.gc_divisor is the denominator in the equation. Setting this value to 1
; when the session.gc_divisor value is 100 will give you approximately a 1% chance
; the gc will run on any give request. Increasing this value to 1000 will give you
; a 0.1% chance the gc will run on any give request. For high volume production servers,
; this is a more efficient approach.
; Default Value: 100
; Development Value: 1000
; Production Value: 1000
; https://php.net/session.gc-divisor
session.gc_divisor = 1000
; After this number of seconds, stored data will be seen as 'garbage' and
; cleaned up by the garbage collection process.
; https://php.net/session.gc-maxlifetime
session.gc_maxlifetime = 1440
; NOTE: If you are using the subdirectory option for storing session files
; (see session.save_path above), then garbage collection does not
; happen automatically. You will need to do your own garbage
; collection through a shell script, cron entry, or some other method.
; For example, the following script would is the equivalent of
; setting session.gc_maxlifetime to 1440 (1440 seconds = 24 minutes):
; find /path/to/sessions -cmin +24 -type f | xargs rm
; Check HTTP Referer to invalidate externally stored URLs containing ids.
; HTTP_REFERER has to contain this substring for the session to be
; considered as valid.
; https://php.net/session.referer-check
session.referer_check =
; How many bytes to read from the file.
; https://php.net/session.entropy-length
;session.entropy_length = 32
; Specified here to create the session id.
; https://php.net/session.entropy-file
; Defaults to /dev/urandom
; On systems that don't have /dev/urandom but do have /dev/arandom, this will default to /dev/arandom
; If neither are found at compile time, the default is no entropy file.
; On windows, setting the entropy_length setting will activate the
; Windows random source (using the CryptoAPI)
;session.entropy_file = /dev/urandom
; Set to {nocache,private,public,} to determine HTTP caching aspects
; or leave this empty to avoid sending anti-caching headers.
; https://php.net/session.cache-limiter
session.cache_limiter = nocache
; Document expires after n minutes.
; https://php.net/session.cache-expire
session.cache_expire = 180
; trans sid support is disabled by default.
; Use of trans sid may risk your users' security.
; Use this option with caution.
; - User may send URL contains active session ID
; to other person via. email/irc/etc.
; - URL that contains active session ID may be stored
; in publicly accessible computer.
; - User may access your site with the same session ID
; always using URL stored in browser's history or bookmarks.
; https://php.net/session.use-trans-sid
session.use_trans_sid = 0
; Select a hash function for use in generating session ids.
; Possible Values
; 0 (MD5 128 bits)
; 1 (SHA-1 160 bits)
; This option may also be set to the name of any hash function supported by
; the hash extension. A list of available hashes is returned by the hash_algos()
; function.
; https://php.net/session.hash-function
session.hash_function = 0
; Define how many bits are stored in each character when converting
; the binary hash data to something readable.
; Possible values:
; 4 (4 bits: 0-9, a-f)
; 5 (5 bits: 0-9, a-v)
; 6 (6 bits: 0-9, a-z, A-Z, "-", ",")
; Default Value: 4
; Development Value: 5
; Production Value: 5
; https://php.net/session.hash-bits-per-character
session.hash_bits_per_character = 5
; The URL rewriter will look for URLs in a defined set of HTML tags.
; form/fieldset are special; if you include them here, the rewriter will
; add a hidden
field with the info which is otherwise appended
; to URLs. If you want XHTML conformity, remove the form entry.
; Note that all valid entries require a "=", even if no value follows.
; Default Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,form=,fieldset="
; Development Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
; Production Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
; https://php.net/url-rewriter.tags
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry"
; Enable upload progress tracking in $_SESSION
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: On
; https://php.net/session.upload-progress.enabled
;session.upload_progress.enabled = On
; Cleanup the progress information as soon as all POST data has been read
; (i.e. upload completed).
; Default Value: On
; Development Value: On
; Production Value: On
; https://php.net/session.upload-progress.cleanup
;session.upload_progress.cleanup = On
; A prefix used for the upload progress key in $_SESSION
; Default Value: "upload_progress_"
; Development Value: "upload_progress_"
; Production Value: "upload_progress_"
; https://php.net/session.upload-progress.prefix
;session.upload_progress.prefix = "upload_progress_"
; The index name (concatenated with the prefix) in $_SESSION
; containing the upload progress information
; Default Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS"
; Development Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS"
; Production Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS"
; https://php.net/session.upload-progress.name
;session.upload_progress.name = "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS"
; How frequently the upload progress should be updated.
; Given either in percentages (per-file), or in bytes
; Default Value: "1%"
; Development Value: "1%"
; Production Value: "1%"
; https://php.net/session.upload-progress.freq
;session.upload_progress.freq = "1%"
; The minimum delay between updates, in seconds
; Default Value: 1
; Development Value: 1
; Production Value: 1
; https://php.net/session.upload-progress.min-freq
;session.upload_progress.min_freq = "1"
; Only write session data when session data is changed. Enabled by default.
; https://php.net/session.lazy-write
;session.lazy_write = On
[Assertion]
; Switch whether to compile assertions at all (to have no overhead at run-time)
; -1: Do not compile at all
; 0: Jump over assertion at run-time
; 1: Execute assertions
; Changing from or to a negative value is only possible in php.ini! (For turning assertions on and off at run-time, see assert.active, when zend.assertions = 1)
; Default Value: 1
; Development Value: 1
; Production Value: -1
; https://php.net/zend.assertions
zend.assertions = -1
; Assert(expr); active by default.
; https://php.net/assert.active
;assert.active = On
; Throw an AssertationException on failed assertions
; https://php.net/assert.exception
;assert.exception = On
; Issue a PHP warning for each failed assertion. (Overridden by assert.exception if active)
; https://php.net/assert.warning
;assert.warning = On
; Don't bail out by default.
; https://php.net/assert.bail
;assert.bail = Off
; User-function to be called if an assertion fails.
; https://php.net/assert.callback
;assert.callback = 0
; Eval the expression with current error_reporting(). Set to true if you want
; error_reporting(0) around the eval().
; https://php.net/assert.quiet-eval
;assert.quiet_eval = 0
[COM]
; path to a file containing GUIDs, IIDs or filenames of files with TypeLibs
; https://php.net/com.typelib-file
;com.typelib_file =
; allow Distributed-COM calls
; https://php.net/com.allow-dcom
;com.allow_dcom = true
; autoregister constants of a components typlib on com_load()
; https://php.net/com.autoregister-typelib
;com.autoregister_typelib = true
; register constants casesensitive
; https://php.net/com.autoregister-casesensitive
;com.autoregister_casesensitive = false
; show warnings on duplicate constant registrations
; https://php.net/com.autoregister-verbose
;com.autoregister_verbose = true
; The default character set code-page to use when passing strings to and from COM objects.
; Default: system ANSI code page
;com.code_page=
[mbstring]
; language for internal character representation.
; This affects mb_send_mail() and mbstring.detect_order.
; https://php.net/mbstring.language
;mbstring.language = Japanese
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global internal_encoding instead.
; internal/script encoding.
; Some encoding cannot work as internal encoding. (e.g. SJIS, BIG5, ISO-2022-*)
; If empty, default_charset or internal_encoding or iconv.internal_encoding is used.
; The precedence is: default_charset < internal_encoding < iconv.internal_encoding
;mbstring.internal_encoding =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global input_encoding instead.
; http input encoding.
; mbstring.encoding_traslation = On is needed to use this setting.
; If empty, default_charset or input_encoding or mbstring.input is used.
; The precedence is: default_charset < intput_encoding < mbsting.http_input
; https://php.net/mbstring.http-input
;mbstring.http_input =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global output_encoding instead.
; http output encoding.
; mb_output_handler must be registered as output buffer to function.
; If empty, default_charset or output_encoding or mbstring.http_output is used.
; The precedence is: default_charset < output_encoding < mbstring.http_output
; To use an output encoding conversion, mbstring's output handler must be set
; otherwise output encoding conversion cannot be performed.
; https://php.net/mbstring.http-output
;mbstring.http_output =
; enable automatic encoding translation according to
; mbstring.internal_encoding setting. Input chars are
; converted to internal encoding by setting this to On.
; Note: Do not use automatic encoding translation for
; portable libs/applications.
; https://php.net/mbstring.encoding-translation
;mbstring.encoding_translation = Off
; automatic encoding detection order.
; "auto" detect order is changed according to mbstring.language
; https://php.net/mbstring.detect-order
;mbstring.detect_order = auto
; substitute_character used when character cannot be converted
; one from another
; https://php.net/mbstring.substitute-character
;mbstring.substitute_character = none
; overload(replace) single byte functions by mbstring functions.
; mail(), ereg(), etc are overloaded by mb_send_mail(), mb_ereg(),
; etc. Possible values are 0,1,2,4 or combination of them.
; For example, 7 for overload everything.
; 0: No overload
; 1: Overload mail() function
; 2: Overload str() functions ; 4: Overload ereg() functions
; https://php.net/mbstring.func-overload
;mbstring.func_overload = 0
; enable strict encoding detection.
; Default: Off
;mbstring.strict_detection = On
; This directive specifies the regex pattern of content types for which mb_output_handler()
; is activated.
; Default: mbstring.http_output_conv_mimetype=^(text/|application/xhtml+xml)
;mbstring.http_output_conv_mimetype=
[gd]
; Tell the jpeg decode to ignore warnings and try to create
; a gd image. The warning will then be displayed as notices
; disabled by default
; https://php.net/gd.jpeg-ignore-warning
;gd.jpeg_ignore_warning = 0
[exif]
; Exif UNICODE user comments are handled as UCS-2BE/UCS-2LE and JIS as JIS.
; With mbstring support this will automatically be converted into the encoding
; given by corresponding encode setting. When empty mbstring.internal_encoding
; is used. For the decode settings you can distinguish between motorola and
; intel byte order. A decode setting cannot be empty.
; https://php.net/exif.encode-unicode
;exif.encode_unicode = ISO-8859-15
; https://php.net/exif.decode-unicode-motorola
;exif.decode_unicode_motorola = UCS-2BE
; https://php.net/exif.decode-unicode-intel
;exif.decode_unicode_intel = UCS-2LE
; https://php.net/exif.encode-jis
;exif.encode_jis =
; https://php.net/exif.decode-jis-motorola
;exif.decode_jis_motorola = JIS
; https://php.net/exif.decode-jis-intel
;exif.decode_jis_intel = JIS
[Tidy]
; The path to a default tidy configuration file to use when using tidy
; https://php.net/tidy.default-config
;tidy.default_config = /usr/local/lib/php/default.tcfg
; Should tidy clean and repair output automatically?
; WARNING: Do not use this option if you are generating non-html content
; such as dynamic images
; https://php.net/tidy.clean-output
tidy.clean_output = Off
[soap]
; Enables or disables WSDL caching feature.
; https://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-enabled
soap.wsdl_cache_enabled=1
; Sets the directory name where SOAP extension will put cache files.
; https://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-dir
soap.wsdl_cache_dir="/tmp"
; (time to live) Sets the number of second while cached file will be used
; instead of original one.
; https://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-ttl
soap.wsdl_cache_ttl=86400
; Sets the size of the cache limit. (Max. number of WSDL files to cache)
soap.wsdl_cache_limit = 5
[sysvshm]
; A default size of the shared memory segment
;sysvshm.init_mem = 10000
[ldap]
; Sets the maximum number of open links or -1 for unlimited.
ldap.max_links = -1
[mcrypt]
; For more information about mcrypt settings see https://php.net/mcrypt-module-open
; Directory where to load mcrypt algorithms
; Default: Compiled in into libmcrypt (usually /usr/local/lib/libmcrypt)
;mcrypt.algorithms_dir=
; Directory where to load mcrypt modes
; Default: Compiled in into libmcrypt (usually /usr/local/lib/libmcrypt)
;mcrypt.modes_dir=
[dba]
;dba.default_handler=
[opcache]
; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled
;opcache.enable=0
; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled for the CLI version of PHP
;opcache.enable_cli=0
; The OPcache shared memory storage size.
;opcache.memory_consumption=64
; The amount of memory for interned strings in Mbytes.
;opcache.interned_strings_buffer=4
; The maximum number of keys (scripts) in the OPcache hash table.
; Only numbers between 200 and 100000 are allowed.
;opcache.max_accelerated_files=2000
; The maximum percentage of "wasted" memory until a restart is scheduled.
;opcache.max_wasted_percentage=5
; When this directive is enabled, the OPcache appends the current working
; directory to the script key, thus eliminating possible collisions between
; files with the same name (basename). Disabling the directive improves
; performance, but may break existing applications.
;opcache.use_cwd=1
; When disabled, you must reset the OPcache manually or restart the
; webserver for changes to the filesystem to take effect.
;opcache.validate_timestamps=1
; How often (in seconds) to check file timestamps for changes to the shared
; memory storage allocation. ("1" means validate once per second, but only
; once per request. "0" means always validate)
;opcache.revalidate_freq=2
; Enables or disables file search in include_path optimization
;opcache.revalidate_path=0
; If disabled, all PHPDoc comments are dropped from the code to reduce the
; size of the optimized code.
;opcache.save_comments=1
; If enabled, a fast shutdown sequence is used for the accelerated code
;opcache.fast_shutdown=0
; Allow file existence override (file_exists, etc.) performance feature.
;opcache.enable_file_override=0
; A bitmask, where each bit enables or disables the appropriate OPcache
; passes
;opcache.optimization_level=0xffffffff
;opcache.inherited_hack=1
;opcache.dups_fix=0
; The location of the OPcache blacklist file (wildcards allowed).
; Each OPcache blacklist file is a text file that holds the names of files
; that should not be accelerated. The file format is to add each filename
; to a new line. The filename may be a full path or just a file prefix
; (i.e., /var/www/x blacklists all the files and directories in /var/www
; that start with 'x'). Line starting with a ; are ignored (comments).
;opcache.blacklist_filename=
; Allows exclusion of large files from being cached. By default all files
; are cached.
;opcache.max_file_size=0
; Check the cache checksum each N requests.
; The default value of "0" means that the checks are disabled.
;opcache.consistency_checks=0
; How long to wait (in seconds) for a scheduled restart to begin if the cache
; is not being accessed.
;opcache.force_restart_timeout=180
; OPcache error_log file name. Empty string assumes "stderr".
;opcache.error_log=
; All OPcache errors go to the Web server log.
; By default, only fatal errors (level 0) or errors (level 1) are logged.
; You can also enable warnings (level 2), info messages (level 3) or
; debug messages (level 4).
;opcache.log_verbosity_level=1
; Preferred Shared Memory back-end. Leave empty and let the system decide.
;opcache.preferred_memory_model=
; Protect the shared memory from unexpected writing during script execution.
; Useful for internal debugging only.
;opcache.protect_memory=0
; Allows calling OPcache API functions only from PHP scripts which path is
; started from specified string. The default "" means no restriction
;opcache.restrict_api=
; Mapping base of shared memory segments (for Windows only). All the PHP
; processes have to map shared memory into the same address space. This
; directive allows to manually fix the "Unable to reattach to base address"
; errors.
;opcache.mmap_base=
; Enables and sets the second level cache directory.
; It should improve performance when SHM memory is full, at server restart or
; SHM reset. The default "" disables file based caching.
;opcache.file_cache=
; Enables or disables opcode caching in shared memory.
;opcache.file_cache_only=0
; Enables or disables checksum validation when script loaded from file cache.
;opcache.file_cache_consistency_checks=1
; Enables or disables copying of PHP code (text segment) into HUGE PAGES.
; This should improve performance, but requires appropriate OS configuration.
;opcache.huge_code_pages=1
[curl]
; A default value for the CURLOPT_CAINFO option. This is required to be an
; absolute path.
;curl.cainfo =
[openssl]
; The location of a Certificate Authority (CA) file on the local filesystem
; to use when verifying the identity of SSL/TLS peers. Most users should
; not specify a value for this directive as PHP will attempt to use the
; OS-managed cert stores in its absence. If specified, this value may still
; be overridden on a per-stream basis via the "cafile" SSL stream context
; option.
;openssl.cafile=
; If openssl.cafile is not specified or if the CA file is not found, the
; directory pointed to by openssl.capath is searched for a suitable
; certificate. This value must be a correctly hashed certificate directory.
; Most users should not specify a value for this directive as PHP will
; attempt to use the OS-managed cert stores in its absence. If specified,
; this value may still be overridden on a per-stream basis via the "capath"
; SSL stream context option.
;openssl.capath=
; Local Variables:
; tab-width: 4
; End:
VPS および専用アカウントでメインの php.ini を編集するための役立つガイドもあります。